Sir Winston Churchill the drunk? Nazi propaganda did a very good job painting Churchill as a drunk and glutton, in the Nazi Propaganda Ministry’s block buster of about the Boer War “Uncle Kruger” Ohm Krüger (1941), Churchill is depicted as a Concentration Camp Commandant, complete with bulldog, which whilst feasting himself he also feeds prime cuts to his bulldog, all the time whilst his Boer women and children in the camp are being starved to death.1

In another propaganda poster – this one from Serbia during World War 2, called ‘Churchill behind the mask’. After taking off his mask shown to the public, halo and all, a Jewish star now above his head and showing a drunken, haggard face and whiskey bottle in his pocket.
The poster falls part of an anti-Semitic campaign called ‘The Grand Anti-Masonic Exhibition’, which opened in Belgrade, in occupied Serbia on 22 October 1941. Financed by Nazi Germans and opened with the support of collaborationist leader Milan Nedić. Although being anti-Masonic in its title, the primary purpose was to promote antisemitic ideology and intensify hatred of Jews – ironically Churchill was a Freemason for a short time, but that is coincidental.
A famous quote has also entered the lexicon of Winston Churchill as proof positive he was a ‘drunk’ (bear in mind its the only quote) – Churchill was accompanied Ronald Golding his bodyguard and whilst exiting the Parliament building and he was confronted by Bessie Braddock, a fellow MP, who said:
Bessie Braddock: “Winston, you are drunk, and what’s more you are disgustingly drunk.”
Churchill replied: “Bessie, my dear, you are ugly, and what’s more, you are disgustingly ugly. But tomorrow I shall be sober and you will still be disgustingly ugly.”
A lush surely this Churchill fellow must be, he said so – right? Turns out Ronald Golding later admitted Churchill was not drunk that night, merely exhausted and unsteady. Being tired he gave Braddock both barrels, and what he quoted was from his rather photographic memory, and it was a W.C Fields character in the movie “its a gift” who when told he is drunk, responds, “Yeah, and you’re crazy. But I’ll be sober tomorrow and you’ll be crazy the rest of your life.” So, the Bessie Braddock encounter was really Churchill editing and reciting W. C. Fields.2
Was Churchill known for drinking? In fact no member of his family ever saw Churchill the worse for drink, they saw him drink yes, but never ‘drunk’. Richard M. Langworth spent 40 years researching Churchill and only found one reference of him been drunk … it came from a military staffer who helped Churchill and Eden on a wobbly walk back to the British Embassy in Teheran, this after a late-night of mutual toasts with the Russians.3
Whilst it is true that at the on-set of the South African War (1899-1902) – Churchill, the son of a Baron and part of British well-to-do society, aged 25 and acting as a correspondent on the Morning Post took with him 36 bottles of wine, 18 bottles of ten-year old scotch, and 6 bottles of vintage brandy. Such was the arrogance of aristocracy in addition to this booze cabinet he also took a valet with him to South Africa. However, if you step back from this and see that Churchill took with him a full year’s supply, then that ‘booze’ cabinet hardly makes a mark.4
With this Churchill became synonymous with two things according to modern writers – alcohol and war.
In one famous wartime episode during World War 2, when George VI set a personal example to the troops by giving up alcohol, Churchill declared the whole idea absurd and announced he would not be giving up drink just because the King had.5
He also became synonymous with excess when it came to food, cigars and alcohol, he was known to consume high degrees of relatively low ABV Champagne and watered down brandy. On the food front he detested the idea of the ‘French’ manner of serving seven courses starting with an aperitif and ending with a small dessert. On the ‘formal 7 course’ menu he would start with the meal he enjoyed the most and end on the one he enjoyed least.6
He started the day (every-day) with a small whiskey and water, his daughter would recall it as the “Papa Cocktail” – a smidgen of Johnnie Walker covering the bottom of a tumbler, which was then filled with water and sipped throughout the morning. This practice Winston Churchill learned as a Victorian habit – as a young man in India and South Africa (see My Early Life) he writes that the water was unfit to drink, and one had to add whisky and, “by dint of careful application I learned to like it.”7 Jock Colville, his private secretary would say of the ‘papa cocktail’ that it was so watered down it was akin to mouthwash.8
He however was renowned, not for drinking whiskey, but for drinking brandy and champagne both at lunchtime and dinner, and he was renowned for putting away copious amounts of it. He averaged on 500ml of 12.5% ABV Pol Roger Champagne for lunch and 500ml of Pol Roger Champagne for dinner along with a couple of diluted brandy glasses per day – in all this is estimated about 150ml AA per day. It certainly is ‘heavy drinking’ by any standard but in context of his time Russian delegations meeting him, thought of him as a ‘lightweight’ on this front. Having also said that, large amounts of adult population in South Africa still consume a bottle of wine and a couple of spirit chasers a day – 150ml AA. Only on reaching 76 years of age did Churchill decide to ‘cut down’ a little and said:
“I am trying to cut down on alcohol. I have knocked off brandy and take Cointreau instead. I disliked whiskey at first. It was only when I was a subaltern in India, and there was a choice between dirty water and dirty water with some whiskey in it, that I got to like it. I have always, since that time, made a point of keeping in practice.”9
Churchill would also not “nurse” a bottle of alcohol the way a alcoholic would, and seldom drank ‘neat’ spirits (preferring not to), unlike alcoholics he also did not drink randomly during the day, sticking to mealtimes instead, and even then none of his colleagues ever reported seeing Churchill the worse for drink. Thus Churchill’s famous quip:
“I have taken more out of alcohol than alcohol has taken out of me.”10
Very famously, Churchill was knocked down by a car New York in 1931 during the American Prohibition 1920 – 1933 on alcohol (he was looking the wrong way), Dr. Otto C. Pickhardt attended to him, actually issued a medical note that Churchill’s medical condition “necessitates the use of alcoholic spirits especially at mealtimes,” specifying 250cc per day as the minimum. A little cheeky to overcome the rigours of Prohibition perhaps, but this is not a sign of dependency – 5 years after this incident in 1936 he took a bet with Rothermere that he could abstain from hard spirits for a year – which apparently he did.11

After World War 2, he developed a reputation for really enjoying food and drink, One visitor from the period noted: “There is always some alcohol in his blood, and it reaches its peak late in the evening after he has had two or three scotches, several glasses of champagne, at least two brandies, and a highball… but his family never sees him the worst for drink.”
That is the point with Churchill, he drank copious amounts of alcohol – no doubt, but he ‘held his booze’ remarkably well, he was never really totally inebriated or ‘drunk’ in fact he detested drunks and could not stand been out of control of his faculties and senses. He was raised as an aristocrat, he believed drunkenness to be contemptible and disgusting, and a fault in which no gentleman indulged.
He also had a very healthy mental appreciation for alcohol and remarked, “my father taught me to have the utmost contempt for people who get drunk.” adding to this he said that a glass of Champagne lifts the spirits, sharpens the wits, but “a bottle produces the opposite effect.”12 Here we also note that Churchill throughout his life kept his wits about him and kept them as sharp as ever.
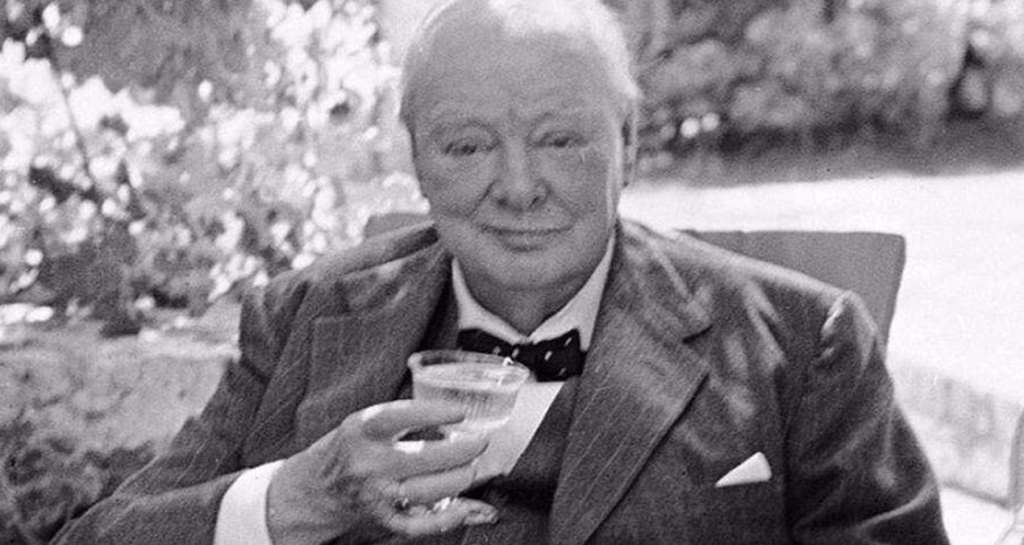

The image of excess is often even associated with Churchill’s disposition to smoking cigars. However very few people know that he seldom smoked more than a third of a cigar, allowing the cigar to burn itself out instead and if anything he took to chewing the end, using it more as image prop than anything else.13
On the physical health front, Churchill did have a heart attack during World War 2, how much of that was excess and how much of it stress is anyone’s guess, however he did recover remarkably well, Dr. Mather, his Doctor reported that Churchill’s blood pressure was a very healthy and very consistent 140/80 well into his eighties.14 In fact most of Churchill’s accompanying younger male military personnel and politicians complained that they could hardly keep up with him, his energy and pace, the speed at which he did everything was legendary. He lived to 90 years old, and died of a stroke – a very long and fruitful innings and not one marred by any alcohol related sickness like liver failure/disease.16
Was he an alcoholic? The general opinion amongst some medical practitioners and historians is that he was not. He demonstrated no real medical signs of a person associated with alcoholism. Did he ‘abuse’ alcohol in our 21st century understanding of excessive drinking and functional alcoholism – yes, no doubt in this context you would place him as someone who abused alcohol for his own edification and enjoyment (of course he would have no idea what you were talking about, as a Victorian born in 1874 faced with a 2024 definition of alcoholism – the modern-day idea simply would not compute).
As to the propaganda, the relentless drive by Hitler and his Nazi Propaganda Ministry to paint Churchill as a glutton and a drunk – rather surprisingly that is the legacy which carries to this day. As an example I once posted Churchill’s medals on a Boer War social media group, it was met with a particular nasty Anglophobic Afrikaner who warned users that Churchill was a rabid alcoholic and his alcohol addled, warmongering mind was responsible for the deaths of hundreds of thousands of people – the devil reincarnate – and I should be ‘very weary’ of who I regard as ‘my hero’ or he would have a few more things to say about him.
Now, I’m a South African – the simple fact he thinks of Churchill as ‘mine’ denotes a massive bias on his behalf and ironically I fear alcohol in the form of far too much ‘branders’ has fuelled his outlook – however, it is interesting to note that in this grouping Churchill’s legacy is still viewed by some in the light of propaganda and not the actual historiography of the man.
Written and Researched by Peter Dickens
Footnotes
- H Steinhoff, Ohm Krüger (1941, Tobis Film, Screenshot from YouTube) ↩︎
- R Langworth, Drunk and Ugly: The Rumour Mill, International Churchill Society 10 January 2011 [accessed 12 August 2024] ↩︎
- Langworth, Drunk and Ugly: The Rumour Mill ↩︎
- PA Dickens, How South Africa Forged Churchill, 22 April 2018 [accessed 12 August 2024] ↩︎
- Langworth, Drunk and Ugly: The Rumour Mill ↩︎
- B Johnson, The Churchill Factor: How One Man Made History (London: Hodder & Stoughton), 2015 ↩︎
- WS Churchill, My Early Life: 1874-1904 (London: Thornton Butterworth) 1930 ↩︎
- M Richards, Alcohol Abuser, International Churchill Society 29 August 2008 [accessed 12 August 2024] ↩︎
- Langworth, Drunk and Ugly: The Rumour Mill ↩︎
- Richards, Alcohol Abuser ↩︎
- Ibid ↩︎
- Idid ↩︎
- Ibid ↩︎
- Ibid ↩︎
- Johnson, The Churchill Factor ↩︎