Ox Wagons to Steel Commandos
So what does the 1938 Great Trek Centenary have in common with Sailor Malan’s returning war veterans anti-apartheid movement – The Torch Commando?
Well, it’s all in the name – ‘Steel Commando’ – so what is a Steel Commando and what the heck does it have to do with the famous 1938 Great Trek Centenary defining Afrikanerdom and Sailor Malan’s later ’Torch Commando’ in 1951.
So here’s the backdrop:
The 1938 Great Trek Centenary
In 1938, the Broederbond under the directive of its Chairman, Henning Klopper sought to use the centenary of Great Trek to unite the ‘Cape Afrikaners’ and the ‘Boere Afrikaners’ under the symbology of the Great trek. In this endeavour artificially creating a shared heritage. He started a Great Trek re-enactment with two Ox-Wagons in Cape Town and addressed the large crowd of 20,000 spectators by saying;
“We ask the entire Afrikanerdom to take part in the festival celebration in this spirit. We long that nothing shall hinder the Afrikaner people as a whole from taking part. This movement is born from the People; may the People carry it in their hearts all the way to Pretoria and Blood River. Let us build up a monument for Afrikaner hearts. May this simple trek bind together in love those Afrikaner hearts which do not yet beat together. We dedicate these wagons to our People and to our God.”
By that he hoped to combine the ‘Cape white Afrikaners’ with the ‘Boer white Afrikaners’ in the symbology of the Great Trek under a fabricated Nationalist ideal of Christian Nationalism – and only meant ‘White’ Afrikaners in the Broederbond’s definition of what constituted ‘Afrikanerdom’ and not really the Afrikaans speaking peoples as a ‘whole’ – certainly not the Coloured and Black Afrikaners. The Trek celebration would be pitched as an assertion of Afrikaner white power in South Africa and the Trek as the true path to a overall South African nationhood and identity and ignore the histories of everyone else – black and white – in creating a future South African identity.
In any event the trek re-enactment was very successful in re-aligning white Afrikaner identity under the Christian Nationalist ideal. In the end eight wagons from all around the country threaded their way to Pretoria to lay the cornerstone of the Voortrekker monument – in front of a crowd of 200,000 people. Whilst at the same time, four ox-wagons went to the site of the battle at Blood River for a commemoration service on the 16th December. The wagons stopping in countless towns and villages all around the country along the way to re-name street after street after one or another Voortrekker hero, and laying imprints of the wagons wheels in freshly laid cement at many halts (there are still ‘imprints’ at my hometown in Hermanus).
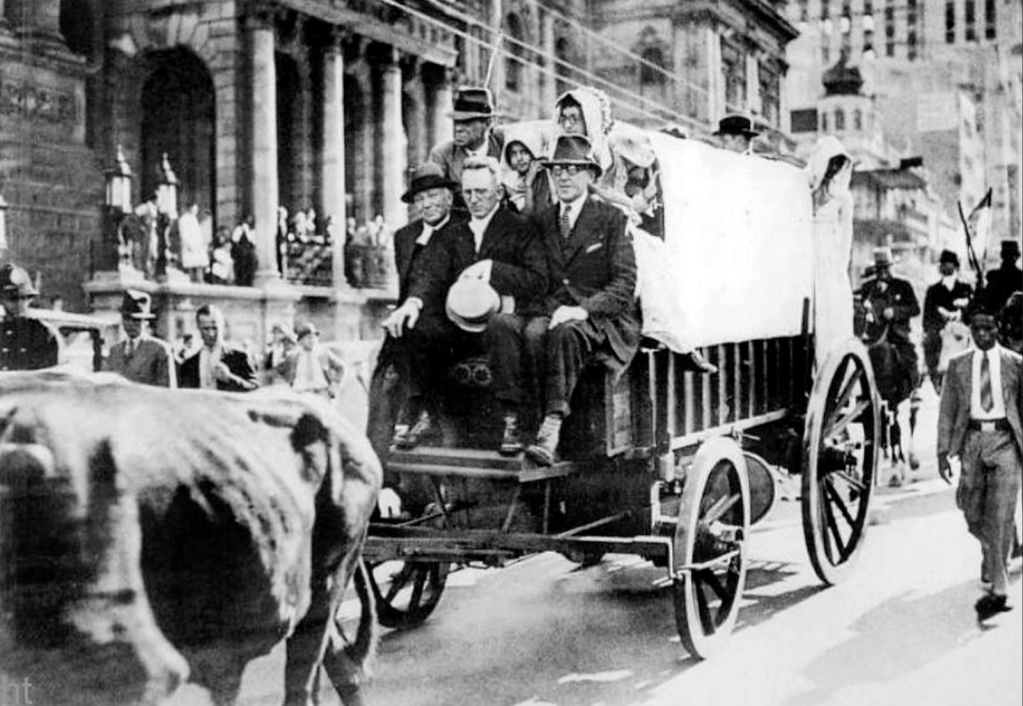




Images: Henning Klopper’s Ox-Wagons named – The ‘Piet Retief’ and the ‘Andries Pretorius, leave Cape Town from the foot of Jan van Riebeeck’s statue to commence the 1938 Centenary of The Great Trek.
The Broederbond had staggered onto the ideal way to ‘unify’ the Afrikaner – a round the country travelling carnival – from the cities to the platteland, on to far flung corners and everything in between. Henning Klopper himself amazed at the reaction and the success of it all – so much so he turned to divine intervention and called it a “sacred happening”.
The Ossewabrandwag
A mere two short years after the Centenary Trek, South Africa was at war with Nazi Germany. Leading up to the war, the South African government was a ‘Fusion’ coalition party between the National Party under Prime Minister Barry Hertzog and General Jan Smuts’ South African Party as his deputy – in an entity called The United Party. The decision to go to war was won by Smuts and a majority vote. Hertzog, whose National Party was already splitting along more radical right lines with the advent of the ‘Pure’ National Party resigned and Smuts became the wartime Prime Minister.
Another one of the primary reasons for the National Party gravitating to radical right-wing lines was the Ox-wagon Great Trek Centennial of 1938. One of the wagon group’s leaders during the trek was Dr Johannes Van Rensburg, a lawyer who had served previously as National Party ‘Secretary of Justice’ in 1933 and was a part-time Union Defence Force officer – he had been to Germany in his capacity as Secretary and met both Hitler and Göring as well as other Nazi officials, he was deeply impressed with both the leadership and discipline offered by Nazism and became an admirer.
So, from the Centenary event in celebration of this coming together of Afrikaner identity under a white-only Afrikaner Nationalism came a cultural movement called the Ossewabrandwag (meaning Ox Wagon Sentinel or ‘Fire Watch’) – abbreviated OB – eventually led by Dr Johannes van Rensberg. Formed in 1938, the ‘Fire’ part of the OB name referred to the rapidly spreading “wildfire” of Christian Nationalism and ‘white’ Afrikanerdom set off by the 1938 Ox-Wagon Centenary Trek, eventually gaining about 250,000 – 300,000 members in total.
The Ossewabrandwag at the on-set was loosely associated to Dr D.F. Malan’s ‘Pure’ National Party. However so as not to tread on one another’s feet, the relationship between the Ossewabrandwag and National Party needed to be formalised. So Dr D.F. Malan met with OB leaders on the 29th October 1940 which resulted in declaration known as the ‘Cradock Protocol’. It specified the two operating spheres of the two respective organisations. They undertook not to meddle in each others affairs and the National Party endeavoured to work for white Afrikanerdom and Christian Nationalism in the “political” sphere while the OB would operate on the “cultural” front.
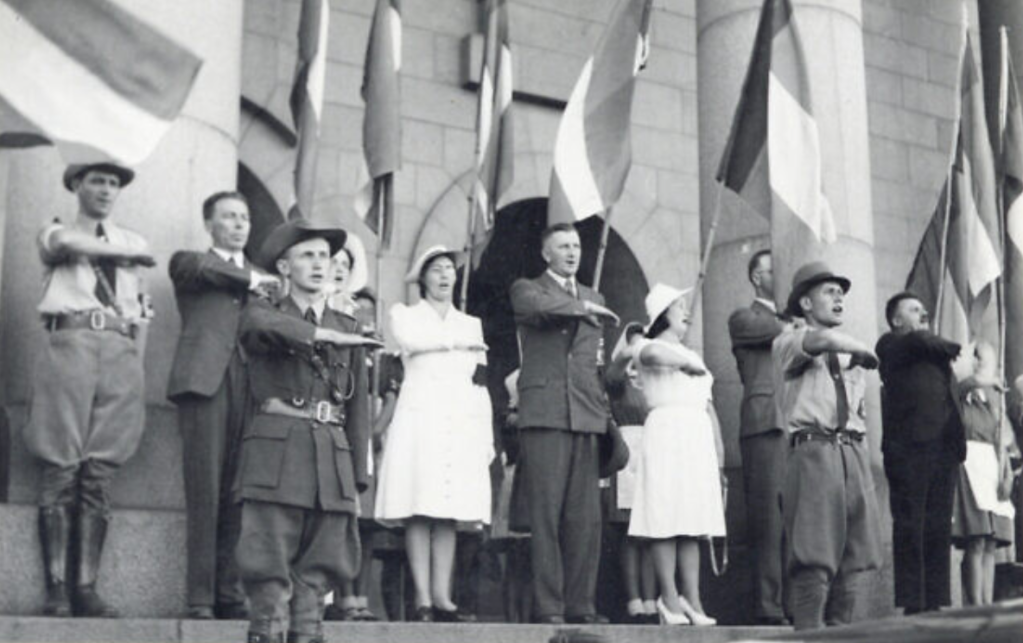


Images: Ossewabrandwag members on parade and taking a Nazi styled salute
Resigning from the Union Defence Force, when war was declared, Dr Johannes Van Rensburg moved to promote the edicts of Nazism in the OB and even directly support the Nazi Germany war effort-ordinating espionage activities for German submarines, the OB under his leadership also evolved away from being a mere ‘cultural movement’ forwarding Nationalist Afrikaner identity, to an active domestic para-military movement with strong Nazi convictions.
Dr Van Rensburg, having resigned as an officer in the Union Defence Force at the start of the war, had always professed been a National Socialist, and as an open admirer of Nazi Germany and Adolph Hitler, the ideas and rituals of membership of the OB had a distinctive Nazi leaning as a result.
Officially, the National Party – when under Hertzog and then under Dr D.F. Malan took the position of ‘neutrality’ as to South Africa’s wartime involvement, but in reality hundreds of thousands of Afrikaner Nationalists were joining openly pro-Nazi Germany movements like the Ossewabrandwag (OB) and its ‘Stormjaers’ (Storm Troopers) military wing, the Nazi Party of South Africa – the South African Christian National Socialist Movement (SANP), the National Socialist Rebels under Robey Leibbrandt, a Nazi Germany insurgent and the Nazi world expansionist order in South Africa – The New Order (NO) under Oswald Pirow who had served as a National Party Defence Minister under Hertzog.
The Steel Commando
The recruitment of white Afrikaners to volunteer for war service became paramount to Union’s Defence Force wartime objectives. On the other side of the Afrikaner coin stood Afrikaners like General Jan Smuts and Dr Ernest Malherbe, who had also been swept up in the enthusiasm of 1938 Great Trek Centenary and the establishment of a unified Afrikaner identity, but not buying into its underpinning Christian Nationalism ideology.
The Malherbe family, for example, being descendants of a French Huguenot and Afrikaners to their core had nothing in common with the Broederbond but had been caught up with all the Afrikanerdom of the 1938 Centenary Trek. At Blood River on 15 December, in the shade of one of the Centenary trek wagons, Dr Ernie Malherbe’s father-in-law, Dominee Paul Nel, baptised their daughter Betty-Jane with water from the Blood River.
When South Africa declared war, Dr Ernie Malherbe and a group of academics, notably Alfred Hoernle and Leo Marquard, persuaded General Smuts to set up, under Malherbe, a corps of information officers to counter subversion in the armed forces generated by the likes of the Ossewabrandwag and the Broederbond and to stimulate the Afrikaner troops and potential white Afrikaner recruits to consider what they were fighting for. Smuts then made Malherbe Director of Military Intelligence with the rank of Colonel. Henceforward South African propaganda which had just been focused on countering Nazi propaganda became much more positive and more South African in its orientation.


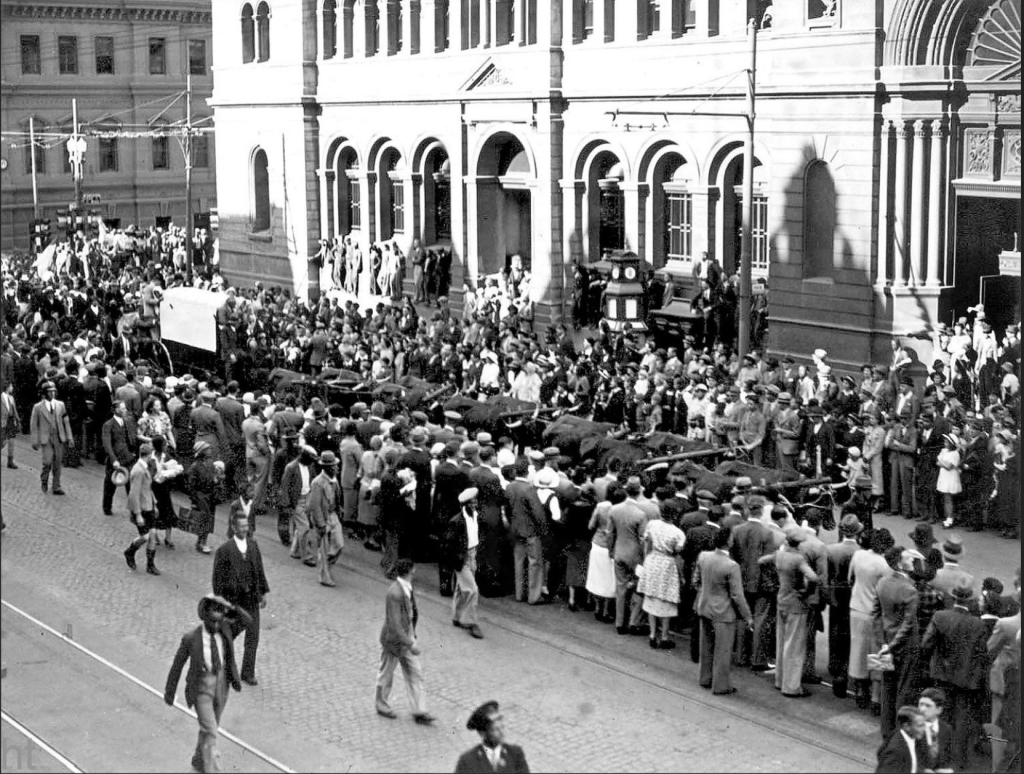
Images; World War 2 recruitment posters targeted at white Afrikaners – note the poster drawing on the ‘the road to South Africa’ commencing from The Battle of Blood River to the Boer War Commandos to the South African Union Army – the title “Still loyal to the path of South Africa” is a direct play on the 1938 Centennial Trek which the Broederbond pitched as “Die Pad van Suid-Afrika,” a symbolic ‘path’ to South Africa’s nationhood taken by the Voortrekkers. This poster attests that joining the Smuts appeal to war is the true path to nationhood.
Critical to Smuts’ call for volunteers to serve in combat regiments was the white Afrikaner nation (as ‘whites’ and ‘coloureds’ were only deemed eligible to carry firearms in the military per segregationist policies and not ‘blacks’). The Union’s Defence Force at the beginning of the war was woefully under strength. Simply put, without the white Afrikaners volunteering for war-time service, South Africa’s wartime commitments for combatants would be ineffectual.
Colonel Malherbe would take a leaf out of the Broederbond’s 1938 Centenary Trek used to ‘unify’ the Afrikaner – a round the country travelling carnival covering just about every town and village in the remotest areas. Only this time Colonel Malherbe intended that the travelling carnival ‘unify’ the Afrikaner behind Smuts’ call to arms to fight with Britain and France on the side of the Allies. He would use armoured cars instead of ox-wagons and his message was almost diametrically opposite to that of the Broederbonds’.
Colonel Malherbe would call his countrywide travelling carnival – The Steel Commando, added to this would be a propaganda and recruitment pamphlet dropping campaign from SAAF aircraft called the Air Commando. The Steel Commando would consist of vehicle to carry a full military band, various armoured cars and a truck converted into a mobile recruitment station. Critical to the Steel Commando would be a contingent of old Republican Boer War veterans (South African War 1899-1902) to give it a sense of ‘Afrikanerdom’ and ‘duty’ to South Africa. The term ‘Commando’ would be given to the convoy – solely because it resonated with old Republics ‘Kommandos’ of the Boer war and as a result had Afrikaner appeal. Isie Smuts (called ‘Ouma’), Jan Smuts’ wife and very popular amongst Afrikaners, young and old, was also positioned as a volksmoeder (people’s mother) a term originated in the Boer War and was initially drawn upon by Afrikaner nationalists to represent ‘the mother of the nation’ connected to the concentration camps – Isie Smuts would become a volksmoeder for the Union’s wartime cause comforting the Afrikaner men and women in uniform and the country’s ‘First Lady.’
This convoy would enter small rural and farming towns with the fanfare of the marching band ahead of it, flanked by the Boer War Republican veterans and the recruiting station behind.
Was it effective in capturing the Afrikaner hearts and minds as the Centenary Trek had been? The truthful answer is – yes. In all the South African standing forces in WW2 comprised 334,000 full-time and voluntary service personnel, 211,000 were White, 77,000 were Blacks and 46,000 were Coloureds and Indians. Of the 211,000 whites, 60% were estimated by Malherbe as being white ‘Afrikaners’ – 126,600 – the majority ethnic group in the South African Union’s Defence Force during World War 2.
To see the effect of a Steel Commando parade, this video outlines one addressed by Smuts as a demonstration of the achievements of recruitment is very telling – note the extensive use of Boer Commando veterans.
What the Steel Commando and Colonel Malherbe’s recruitment drive also did was literally spit the Afrikaner ‘hearts and minds’ in two, one half supporting the National Party’s call to neutrality or the Ossewabrandwag’s call to directly support Nazi Germany – and the other half of white ‘Afrikanerdom’ – supporting the ideals of Union between English and Afrikaans, General Smuts’ policies and the Allied war against Nazi Germany.
Post 1948
The dynamics behind the National Party’s accent to power without a majority vote in 1948 have been vastly researched but suffice it to say that for returning War Veterans from WW2, fighting against Nazism, the advent of a political party with numerous leaders who had been directly and/or indirectly flirting with Nazism during the war as a net result of organisations like the Ox Wagon Sentinel (Ossewabrandwag) and other Neo Nazi factions merging with The National Party was an abhorrent idea and an insult to the sacrifice of their comrades in arms.
The War Veteran’s Action Committee
The outrage to this and the implementation of the first Acts and Bills that would become ‘Apartheid’ would result in a merger of war veteran members of the Springbok Legion veteran’s association and war veterans predominant in the United Party’s political structures in April 1951 – the ‘War Veteran’s Action Committee WVAC (the WVAC was to eventually evolve into The Torch Commando) under the leadership of the charismatic war-time fighter ace – Sailor Malan, a veteran with Afrikaans heritage. Pains were taken to ensure the make-up of the WVAC was 50/50 English/Afrikaans.
The WVAC kicked off their mission with a protest at the Johannesburg Cenotaph on 21st April 1951 during a commemoration service – laying a coffin draped in the national flag as a symbol to depict the death of the Constitution. They ramped their protests up with three torchlight protests in Port Elizabeth, Johannesburg and Durban. At these protests, comprising over 30,000 people in total, a set of resolutions were ratified to take to Cape Town and present to Parliament. The resolutions basically were a warning to the government that the military veteran community would embark on a political struggle unless the National Party government resigns.
Steel Commando (version 2)
But how to whip up support for their cause, and how to whip up the planned mega-torchlight rally in Cape Town to hand over the demands? Here the WVAC took a leaf out of Colonel Malherbe’s Union Defence Force ‘Steel Commando’ recruitment drive. They would not even change the name, the WVAC’s ‘Steel Commando’ would be run along the same lines with military precision. All around the country from far flung places vehicles would converge with the Steel Commando and the Commando itself would drive through multiple towns and villages whipping up publicity and support.
The Steel Commando of the WVAC (Torch Commando) would, as a primary objective also look to recruit, all the Afrikaans war veterans who in their minds may have erroneously voted for the National Party in 1948 and call them back to Smuts’ more moderate politics. To this end, as Colonel Malherbe had done using Republican Boer War veterans, the WVAC would do exactly the same with their version of the Steel Commando and use the old Boer War Veterans. Kommandant Dolf de la Rey, a Boer War veteran whose Commando had been involved in capturing Winston Churchill and national hero was appointed to lead The Steel Commando with Sailor Malan as his 2nd in Command – two Afrikaner war heroes leading the convoy. They would also keep the term Commando when the WVAC formed ‘The Torch Commando’ later as a nod to Afrikaner heritage. Kommandant de la Rey was also affectionally given the term ‘Oom’ by the publicity machine to conjure up respect from the Afrikaner community. This sentiment can be seen in the newspaper reporting outlined as follows:
Of the Steel Commando trip to Cape Town, wrote one newspaper correspondent: “Cape Town staged a fantastic welcome” for Kmdt de la Rey and Group Captain Malan, he related the enthusiasm of the crowd to the same that liberation armies received in Europe. The Johannesburg Star said: “The Commando formed the most democratic contingent ever to march together in the Union. Civil servants found themselves alongside the colored men who swept the streets they were marching so proudly upon.”
“In the front jeep rode Oom Dolf de la Rey, a white-haired old Boer of seventy-four, who looked so startlingly like the late General Jan Smuts that people looked twice at him and then cheered wildly. Oom (Uncle Dolf) was the man who, as a young burgher on commando fifty years before, had captured Winston Churchill, then a war correspondent with the Imperial forces in South Africa.In the second jeep stood a younger man with tousled brown hair, his hazel eyes cold and angry, the man who had been the most famed fighter pilot in all the RAF — Adolph Gysbert Malan, known all over the world as Sailor. He was the real hero of the hour. The people tried to mob him. Men and women, white as well as brown, crowded round his jeep and stretched out their hands to touch him.”
Video: The Steel Commando on-route to Cape Town – note the use of Boer War Kommando veterans.
The ‘Steel Commando’ convoy gathered media attention and grew in size as it converged on Cape Town on the 28th May, a crowd of 4,000 greeted it as it converged in Somerset West before heading to Cape Town that evening. In Cape Town, the Steel Commando arrived to a packed crowd of protesters on The Grand Parade outside the City Hall of between 55,000 to 65,000 people – consisting of whites and coloureds, supporters and veterans alike (veterans were estimated at 10,000). Many holding burning torches as had now become the trademark of the movement. Spooked by it all the National Party were convinced that a military coup was on and as a precautionary measure placed manned machine gun positions around the rooftop of the nearby Houses of Parliament.
Sailor Malan was literally carried on shoulders by cheering crowds to give his speech. Joined by Dolf de la Rey and even future Afrikaner anti-apartheid activist and fellow war veteran Mattheus Uys Krige as well as the English speaking South African war-time soprano and heroine who led them in song – Perla Gibson. In Sailor Malan’s speech to the crowd famously accused the national party government at this rally of;
“Depriving us of our freedom, with a fascist arrogance that we have not experienced since Hitler and Mussolini met their fate”.

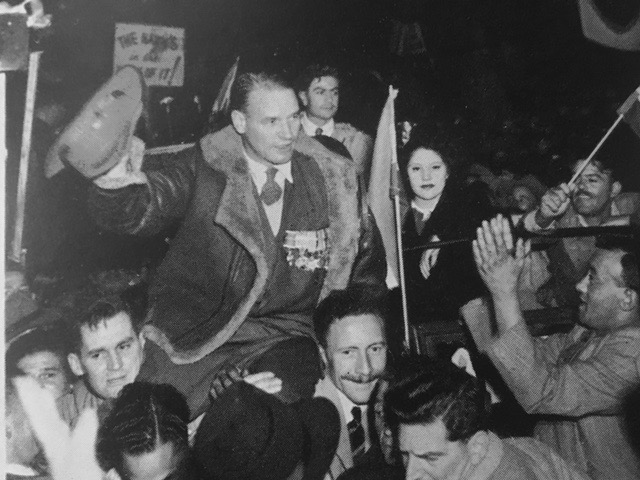
Images: Kommandant Dolf de la Rey and Group Captain Sailor Malan addressing crowds at the Steel Commando in Cape Town
Buoyed by the success of The Steel Commando, The Torch Commando would officially form and would in the course of time rise to 250,000 plus members – so if one asks – was The Steel Commando as successful as its original concept – the pre-war 1938 Ox-Wagon centennial staged by the Broederbond, and whose idea was drawn on by Colonel Malherbe for the Defence Forces’ Steel Commando’ wartime recruitment drive, the answer is yes, and here’s why;
In Conclusion
The white population voting base in 1951 was estimated about 1,000,000 whites. 250,000 whites had polarised to Ossewabrandwag radically politically right on the back of the 1938 Great Trek ‘Ox Wagon’ Centennial .. and 250,000 whites had gravitated radically politically left on the back of The Torch Commando. Literally driving a dividing line between the white voting base (English and Afrikaans) – half in support of Apartheid and half against Apartheid.
It would also splinter the white Afrikaner voter base and the Broederbond’s attempt at a shared Afrikaner National identity, the majority would be swayed by Christian Nationalism as an ideology and keep the National Party in government on a slim margin, becoming more entrenched as the National Party engaged gerrymandering and jack-boot totalitarian politics going into the future – however a significant portion of white Afrikaners would remain ‘Smuts-men’ and resist Christian Nationalism for many years to come – they simply would not buy into the Broederbond’s initial tenants of bringing ‘Afrikanerdom’ under the singular banner of ‘white’ Afrikaner Nationalism and saw it for what it was – a corruption of Afrikaner history, exclusive, hateful and divisive.
The irony, all this fracturing would be caused by the same vehicle to ‘unify’ the white Afrikaner – a travelling carnival appealing directly to the hearts and minds of far flung rural white Afrikaners, initially conceived by the Broederbond to drive an Apartheid agenda starting in Cape Town and picked up in the end, a tad over a decade later, by the Torch Commando to drive an anti-Apartheid agenda – to the same far flung rural white Afrikaners and in a twist of fate ending up back where it all started – Cape Town.
Written and Researched by Peter Dickens


This is what I wrote on the Steel Commando :
No 1,340 PUBLICITY DRIVES. In 1940 Colonel G.C.G.Werdmuller organised several publicity drives, showcasing smart soldiers and South African-made war materiel, from boots to Armoured Cars. With a purpose to recruit, not only into the UDF, but also into industries producing much needed equipment. The first was the ‘Steel Commando’, in which 200 soldiers of the Special Service Battalion and the 50 strong SA Permanent Force Band travelled the country in Ford trucks, covering some 40,000 miles in four months. Then the SAAF ‘Air Commando’, and what became known as the ‘War Train’. The War Train carrying the SSB contingent and Band, with a variety of display equipment from artillery to steel helmets, took six weeks to tour the country, starting in Johannesburg 22nd March, 1941, travelling to the Eastern Transvaal, down through Natal to Durban, then inland through the OFS, South to East London, following the Garden Route, but taking in Oudtshoorn, to Cape Town. Then North through the Karoo to Kimberley, Western, then Northern Transvaal before turning South from Messina to arrive in Pretoria on 7th May. Then a second drive, starting in Pretoria 12th May, via Bechuanaland to the Rhodesia’s, ending in Elizabethville in the Belgian Congo 2nd June A combination of military precision and Railway Time-table accuracy prevailed. At each of the 38 stops, everything was per-arranged and timed to the minute! The troops and band would march, a civil reception was laid on with speeches and then the public, normally starting with the school-children would tour the train and opportunities were there to sign up, to clamber over the equipment and to taste the army biscuits!
Colonel Werdmuller was the actual commander and organiser of the project.
The wagon shown drawn by oxen, is not a trek wagon. The English papers of the time in The Cape and Johannesburg, informed that this example of Afrikaan culture, was in fact a British Army General Service Wagon Mk II. When you compare it with photos of real trek wagons, its quite plain. The newspapers took great pleasure at sneering at it!
I spent far too much time on the Broderbund and the Ossewabrandwag, what charming members of the human race. The Broderbund, which had immense power, protected many and crucified more. Example General Klopper, totally protected after he came back from the Italian POW Camp, and ensured his eventual promotion to Chief of the UDF. Promoted far beyond this level of competence, aged 18 as a school teacher, joined “the Bund”.
On the other, Colonel Jan Breytenbach, probably the finest combat leader, with great training and organisational ability. Told “the Bund” to bugger off, when he at the Army Gymnasium. Whilst one of the ultimate achievers, every possible obstacle was put in his way. 2001 he wrote, The Plunderers. Covos Day. ISBN 1-919874-01-1. A fictional account (?) of the very dubious activities in Southern Angola, the Calpriv Strip and Northern SWA, of politicians, senior members of the SADF, and businessmen. If they did not like him before, it got much worse, The treatment of him whilst in the army and afterwards is worthy of a good book.
Waffeling too much. A last item which has fascinated me for many years.
“17th February 1838 Dingane’s 10,000 strong impi’s marched, making quite brilliant co-ordinated attacks on the Voortrekker parties, over the Bloukrans River and the Bushman’s River, these having had many of their men killed with Retief, 33 Boer men, 75 women and 123 children (also recorded as 41 men, 56 women and 185 children), and 252 servants (see Note to 1.951) killed. An Italian woman Thérèsa Viglione, a trader camped near the Bloukrans laager, with three Italian men and three wagons to trade with the Zulu’s. They left alone during the Zulu attack on Bloukrans. She on a horse galloped to warn Gerrit Maritz’s laager, allowing them to stand to arms. After the attack she nursed the wounded children, gaining the respect of the Voortrekkers, so much so that her image was placed prominently upon the frieze of of the Voortrekker Monument.” And the average Afrikaner knows nothing about her.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Gordon, thank you once again for your considered and insightful reply, wish I had reference you have to the UDF’s Steel Commando, I hunted far and wide and what I had was scant at best. Do please point me to your work, I did a internet search and no joy. Many thanks and kindest regards, Peter
LikeLike
Mr Dickens, a great deal of what I got, I obtained at the Cape Records, which has now been scattered into three locations. At the time I was there, they were just dumping files and books willy nilly into the garbage. It like the SAP in 1994, when everything burnt!
LikeLiked by 1 person