Torch Commando Series – Part 2
War Vets Arise
Very broadly, at the end of The Second World War (1939-1945), returning white South African soldiers found themselves in three broad veteran association camps, either in an returned serviceman organisation called The Springbok Legion – which was highly politicised, steeped in ‘liberal’ and ‘labour’ politics and trade unionist in its manifesto, or as ‘Smuts-men’, they found themselves in the more sedate and larger South African Legion and Memorable Order of Tin Hats (MOTH) veteran associations with their remembrance manifestos, and they returned to the ‘centre-line’ and ‘democratic’ politics of the United Party (UP), their decision to go to war reinforced their conviction to Smuts’ brand of politics and call to arms.
In the chapter on the ‘Nazification of the Afrikaner Right’ we looked at the rise of Nazism and Fascism during the war in South Africa and the amalgamation of Pro-Nazi and Neo-Nazi movements into the Afrikaner Nationalist Party after their shock election win in 1948. The advent of ‘Apartheid’ into South African policy and moves to amend the South African constitution caused widespread angst amongst the ex-servicemen, how had just returned from eradicating the world of Nazism and fascism in WW2 and now they found a home-grown version of it had come into power.
As the National Party consolidated its power after its election win in 1948, sporadic small protests and picketing of ex-servicemen broke out around the country at by-elections and the like protesting the gradual implementation of racially divisive policies around the country. The National Party using plain thuggery drawn from the old Ossewabrandwag structures continued to violently disrupt opposition United Party (UP) and Labour Party (LP) political meetings well beyond the 1948 elections. During various by-elections, UP and LP politicians depended on ex-servicemen to aid them with canvassing and for physical protection from the National Party’s thugs disrupting their political rallies.
On one side of these picketing and ‘protection’ activities around by-elections and political meetings were members of the Springbok Legion (SL), at the time dominated by firebrand Legionnaires, with a significantly strong ‘Jewish’ veteran demographic and with equally strong Liberal and Communist leanings, and they were bent on more aggressive outcomes and military solution to advent of the National Party – whose National Socialist philosophy and whose strong anti-sematic and anti-communism politicking before and during the war posed a significant threat to many of them who had Jewish heritage and/or Communist leanings.
The Springbok Legion
The Springbok Legion (SL) was born along labour manifesto principles during World War 2 seeking (amongst others) equity for Black and White servicemen. The Springbok Legion is initially formed in 1941 within a debating society comprised of members of the 9th Recce Battalion of the South African Tank Corps, at the Kafferskraal training camp near Klerksdorp. By mid 1941, two similar soldiers’ groups formed. One called the ‘Soldiers’ Interests Committee’ formed by members of the 1 South African Brigade (1 SA Bde) in Addis Ababa. The other was the Union of Soldiers, which was also created in Egypt by soldiers of t1 SA Bde. Over time, they agreed to merge these three debating societies/committees together to form ‘The Springbok Legion’.

The aims and objectives of the Springbok Legion were enunciated in its ‘Soldiers Manifesto’. The Springbok Legion was open to all servicemen regardless of race or gender and was avowedly anti-fascist and anti-racist.
Initially led by Jock Isacowitz as the National Chairman – a previously ‘Liberal’ student at Witwatersrand University before joining the South African Army, Isacowitz would be the guiding force behind the establishment of The Torch Commando and later he also became a founding member of the Liberal Party of South Africa.
‘Liberals’ like Isacowitz and Leslie Rubin, as well as future United Party stalwarts like Vic Clapham and anti-Apartheid activists like Brian Bunting made up a significant part of the Springbok Legion, however the Springbok Legion’s membership and leadership also contains Communist Party of South Africa stalwarts who had served in the UDF during the war – key amongst them were Wolfie Kodesh, Rusty Bernstein, Joe Slovo, Cecil Williams, Fred Carneson and Jack Hodgson (all of whom would become founders of the African National Congress’ MK military wing). Cecil Williams for example had served in the Royal Navy during the war, he would become the administrative officer of the Torch Commando’s “Steel Commando”, later he would famously be arrested whilst being ‘chauffeured’ by Nelson Mandela post Sharpeville to get Mandela around to his political meetings.

Although politically very ‘firebrand’ the Springbok Legion often sought out the sage advice of General Jan Smuts, and Smuts had a soft-spot for them calling them “my boys”).
Motivations for joining The Springbok Legion as a veteran’s association differ, Fred Carneson had served as signaller and saw action in East Africa and North Africa, he was badly injured at the Battle of El Alamein. He would highlight the divide in the Afrikaner diaspora caused by the Nazi leaning Ossewabrandwag and the National Party – and would say of the formation of The Springbok Legion:
“(the Springbok Legion) became a vehicle in the South African Army for a lot of progressive thinking, on the race issue as well, amongst white South African soldiers … We took up all sorts of issues there – not only the question of increasing family allowances and things that were hitting their pockets and their families, but on political issues calling for sterner measures against the Broederbond and against the Ossewadrandwag.”

Fred Carneson went on to say:
“the bulk of the South African Army were Afrikaners, not English-speaking, and they were also bloody fed up with this lot (the Ossewabrandwag et al). Some of them were being beaten up when they went to their hometowns and their dorps (villages) by these anti-war elements. The Springbok Legion organized a huge demonstration in Johannesburg which smashed up a Nationalist Party conference, again with whites turning out in force, and a hell of a lot of Afrikaners ex-servicemen. I remember one huge Afrikaner coming along there carrying a rope, and he says, ‘If I put my hands on Malan (referencing Dr. D.F. Malan, the National Party leader) I’m going to hang the bastard!’ … that was the strength of feeling that arose then against those they regarded as traitors, who tried to stab them in the back when they were fighting.”
On the returning white servicemen and women, Afrikaner and English, Carelson would offer an interesting insight on their disposition to race, an insight fundamentally at odds with the National Party and its doctrine, he said:
“… you seldom heard any anti-black sentiment amongst the white soldiers. If you’re in an army and a man’s on your side, you respect him, you see. They saw people of different races fighting together on the same side against the common enemy. This couldn’t but have an effect on their general thinking”.
Wolfie Kodesh offers a differing perspective on why he joined The Springbok Legion, Kodesh is also a combat veteran seeing action in both North Africa and Italy. He becomes politicised during the Italy campaign when he realises that it’s the poor lower class most affected by the bombing campaigns who see their houses bombed flat – whilst the rich upper class and their houses remain relatively unaffected – he identifies in a ‘class’ war and equates it with the Black and Coloured communities in South Africa. He finally decides to join the Springbok Legion and says …
I got involved in the SL to “overcome this racialism, which was like poison. After all, Hitler had been a racist against the Jews – he said he was going to do the same thing to the blacks. Here were the South African whites doing the same thing as Hitler said he would do … this is wrong … and I have to do my bit towards getting rid of it.”
Branches of the SL were established in Johannesburg, Cape Town and Durban. Membership to the SL was open to all races and to women (although few women joined). Black Africans, Indians and Coloureds also joined the SL, men like Peter Kay Selepe, a WW2 veteran and an organiser of the African National Congress (ANC) in Orlando (although few Black members joined – only 98).

The Springbok Legion acted as political pressure group on issues relating to housing, equality, pensions etc and not a political party, members were encouraged to become active in their mainstream political parties – like the United Party and the Labour Party.
The South African Legion
The South African Legion – then known as ‘The South African Legion of the British Empire Services League’, it was founded by Jan Smuts in 1921 was the ‘official’ national body for all South African veterans, and it took a formal approach when dealing with the Nationalist government and its policies as they impacted Black, Indian and Cape Coloured veterans – choosing to try and negotiate with the government via the formal and non-confrontational channels made available to it as the national body for veterans. The South African Legion is South Africa’s prima and largest veterans’ association with 52,000 registered military veterans.
Involved in both The Springbok Legion and the South African Legion is the very influential General Kenneth van der Spuy CBE MC, he is the man who pioneered the formation of South African Air Force (SAAF) under General Smuts’ directives. General Van der Spuy is regarded as the modern father and founder of the SAAF (Smuts would be the Grandfather). After the war he was a key role-player in the establishment of The Springbok Legion and on the National Executive of The South African Legion.
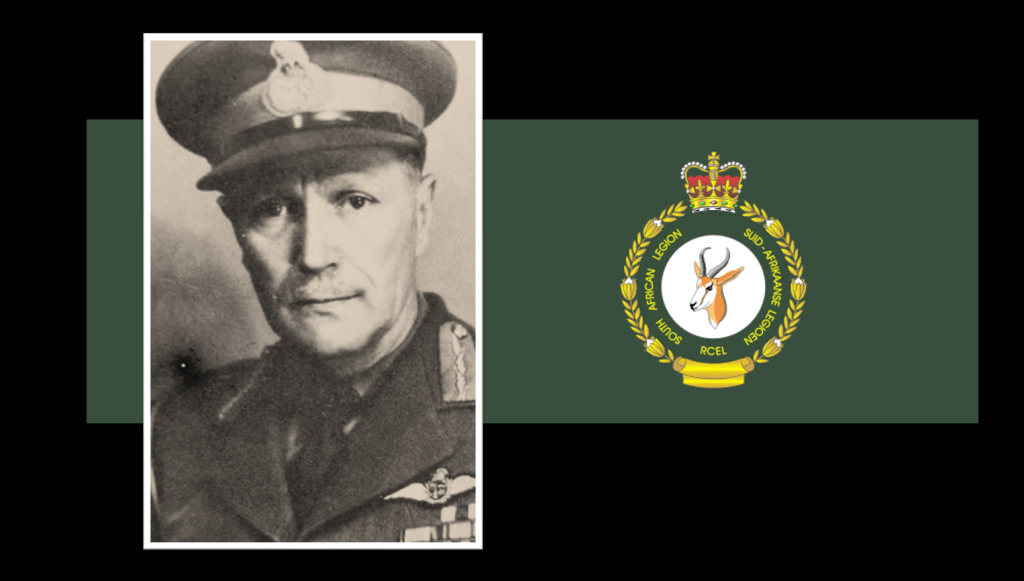
General van der Spuy became increasingly frustrated with The South African Legion position of remaining ‘apolitical’ but quietly’ supporting the anti-apartheid causes in the veteran’s community simply by opening their branches up to them, so he looked to the politically charged Springbok Legion to do what he referred to as the South African Legion’s “painfully correct whisper of polite protest” at the National Party’s policies to become a “shout” of protest instead, thereby encouraging members of the South African Legion to join hands with these concerned veterans in the SL and eventually join the Torch Commando along with General van der Spuy when it is formed.
The United Party
On the other side of the veteran’s diaspora is the largest political Party – the United Party (UP) led by Jan Smuts during wartime, although in the 1943 General Election they come out victorious, Jan Smuts receives an unprecedented level of support, and they command 75% of the house. However, after the end of the war in 1945 the United Party becomes complacent and directionless, even more so after their shock election loss in 1948 to the National Party.

Jan Smuts had intended that his deputy and protégé Jan H Hofmeyr, a ‘Liberal’ in every sense of the word (the nephew of the Afrikaner Bondsman “Onze Jan”), Hofmeyr was the effective PM of South Africa through most of WW2 and like Smuts was farsighted in matters on race – far more than his peers in the United Party. Tragically, he died young at 53 years in 1948. At his funeral Smuts said of him:
“Here was the wonder child of South Africa, with a record with which South Africa shows no parallel, who from his youngest years beat all records, whose achievement in a comparatively brief life shows no parallel in this land, and whose star at the end was still rising ..He has passed on, but his service and the high spirit in which he sought to serve his country and his fellow-men of all races remain our abiding possessions. This is a better and richer country for his service, and his message will not be forgotten.”
It was the first significant setback for the United Party and a more liberal outlook on race, and within two short years of Jan Hofmeyr’s death, Smuts too would pass on – this been the UP’s second and most significant setback. In essence the party had lost both of its key visionaries, and Smuts had been the ‘glue’ holding the party together and giving it direction.
The UP was sorely in need of an injection of young blood and firebrand politics – and it found this in the returning servicemen who were highly politicised influences and equally angered with the National Party’s flirtation with Nazism prior to and during the war. In all they would form a ‘ex-services’ caucus with the United Party and Parliamentary politics.

Notably amongst this UP faction was Captain Harry Oppenheimer, who, aside from being a significant economic and political powerhouse, served as an intelligence officer in the 4th South African armoured brigade during the war. Son of the industrialist Earnest Oppenheimer, Harry became the UP Minister of Parliament for Kimberley, as a prominent South African businessman, industrialist and philanthropist. Oppenheimer was ranked as one of the wealthiest people in the world and was considered South Africa’s foremost industrialist for four decades. He would become the key financial benefactor behind the Torch Commando.
The second notable UP member was Captain Sir de Villiers Graaf, a veteran of North Africa and been taken Prisoner of War (POW) during the fall of Tobruk, given an MBE for his relief efforts amongst prisoners, he would eventually lead the UP, and although not a Torch Commando member, he would become the official liaison officer between the Torch and the UP in 1952.
Also within the UP fold was Major Louis Kane-Berman, a veteran of both the North African and Italy campaigns and Democratic politics pioneers – Louis Kane-Berman would become the National Chairman of the Torch Commando.
Also of significance in this group of UP members was L/Cpl. Colin Eglin who had joined the 6th South African Armoured Division fighting in the Italian Apennines around Florence as part of the Cape Town Highlanders – Colin Eglin “the egg” would become a future Progressive Party powerhouse politician, cutting his political teeth in the UP and Torch Commando. Eglin could already see the malaise and disarray the UP had landed in when he said of the UP:
“morale was low; organisation pathetic; policy and ideology were confused and ambivalent. In this situation, the old- guard leadership looked for someone other than themselves to blame.”

Finally in the UP, Lt. Vic Clapham Jr., who had served in the SA Tank Corps in WW2 as a Lieutenant, and who was the son of the famous World War 1 veteran who started the Comrades Marathon, also Vic Clapham – Vic Clapham Jr. was an ex-Springbok Legionnaire, he had resigned from the SL National Executive in 1945 and he was now United Party stalwart. Vic Clapham would act as the conduit between his old chums in the SL with his new chums in the UP, and the two groups of concerned veterans from the Springbok Legion and the United Party decided to join hands and consolidated in April 1951 to form the ‘War Veteran’s Action Committee – WVAC’ (the WVAC was to evolve into The Torch Commando).
The leadership team of the WVAC was made up of veterans perceived as ‘moderate’ (as opposed to the more firebrand ‘Communists’ in the Springbok Legion) to present a broader appeal across the political spectrum. It’s also a balanced committee between ‘English’ and ‘Afrikaners’ – designed to address the polarisation in Afrikaner politics and bring Afrikaner voters who had served in the military during WW2 back to mainstream and moderate politics.

The leaders appointed were Group Captain Adolph ‘Sailor’ Malan, Major Louis Kane-Berman, Major Ralph Parrott (a UP man who had served in the Transvaal Scottish in the South African Army and was awarded the Military Cross for bravery in the Battle of Tobruk), Major Jacob Pretorius (ex-SAAF and also a UP man) and Lt. Colonel Doreen Dunning – who during the war was the Officer Commanding the South African Women’s Auxiliary Air Force (SAWAAF). Harry Oppenheimer, not wanting to take a forward role pushed for Sailor Malan (Oppenheimer’s former Private Secretary) to take the role as the leader of the WVAC.
In the company of greats, Lt Col. Doreen Dunning (also remembered as Doreen Hooper) is an interesting appointment, she was one of the founders of the South African Women’s Auxiliary Air Force (WAAF) during the Second World War (1939-1945), she was highly respected SAAF officer, wartime heroine and a pioneering female aviator. At the outbreak of war, she had more than 2 000 flying hours to her credit. At the incredibly early age of 24 she was the youngest officer in the British Commonwealth to attain the rank she held.

Fair haired and blue eyed, she had a quiet, forceful personality combined with outstanding ability and tact which made her eminently suitable for the responsible administrative post that she held both in the South African Air Force and now as secretary to The Torch Commando.
Major Louis Kane- Berman is also a significant appointment as he would go on to be the Chairman of The Torch Commando, next to Sailor Malan his history and activities would shape white service-men resistance to Apartheid. He in fact is the powerhouse behind the Torch running its daily and hands-on activities. Louis Kane- Berman was highly popular, the son of Edith Kane-Berman, Chief Commandant of the Red Cross. He attested as a signaller in the Signal’s corps of the South African Army, he would see combat in both North Africa and Italy as a company commander. Post war he gets very involved in rallying ex-servicemen to protect the UP speakers and presents himself as an ideal candidate for WVAC.
Louis Kane-Berman in his later life was also extensively involved in the National War Memorial Fund and he would remain in ‘liberal’ and ‘federal’ politics most of his life and play a key role in the Union Federal Party.
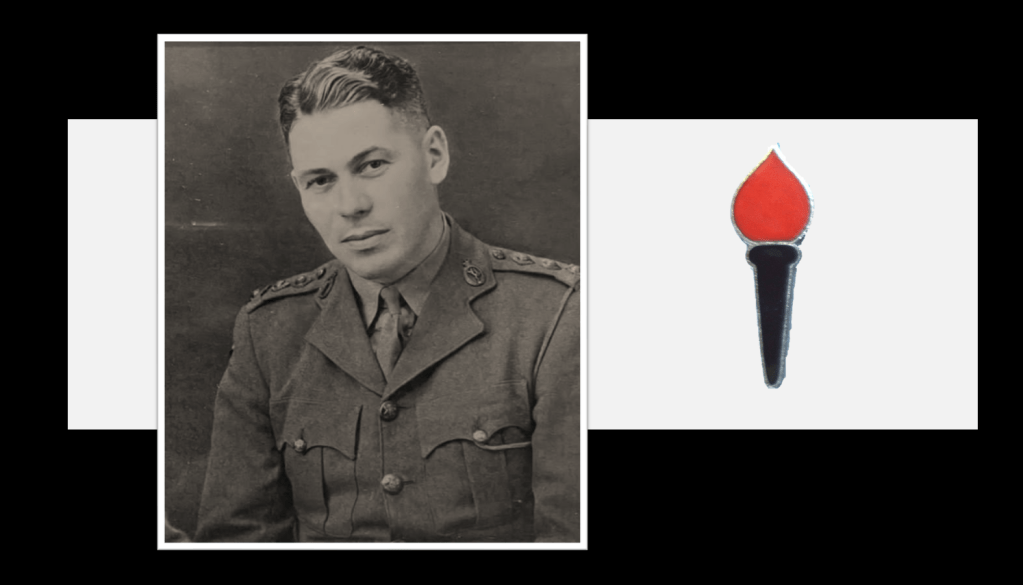
It is important at this stage to cover Sailor Malan’s appointment, and why he is regarded as such a significant war hero and why he is forever linked to The Torch Commando as part of its public façade. Here’s some background on Sailor’s ‘metal’.
Group Captain Sailor Malan
Sailor Malan agreed to join the WVAC only on the proviso that his internal principles were adhered to. These been the political injustices suffered by people of colour in South Africa and resisting the government’s anti-constitutionalism and their drift towards a local brand of Nazism. Sailor is to be the ‘face’ of WVAC as he is highly recognisable and intensely popular across the board – he is the son of an Afrikaner father and a ‘English’ mother and sees himself as a South African first and foremost with strong Afrikaner ties and heritage.
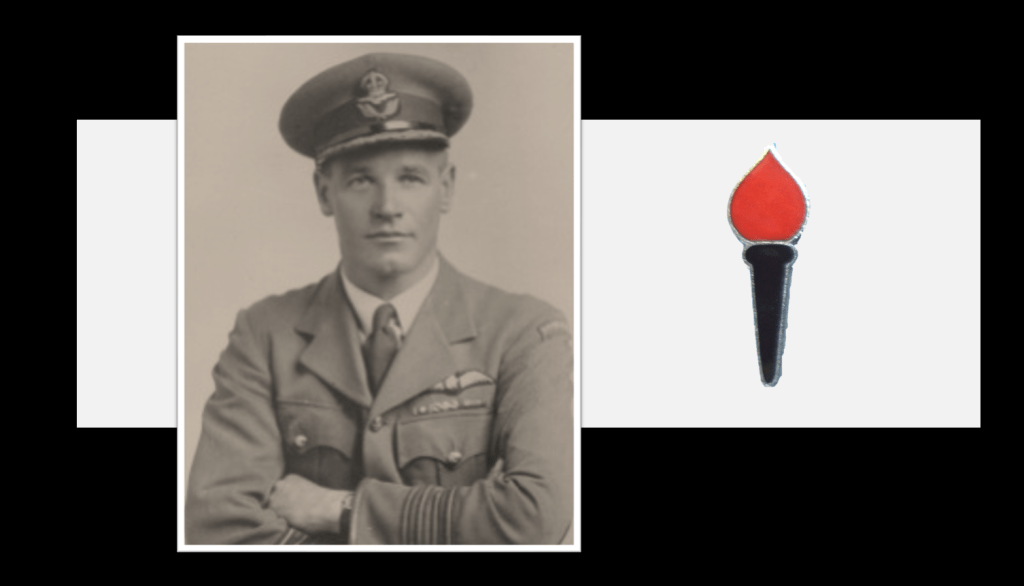

Adolph Gysbert “Sailor” Malan stemmed from Wellington in the Western Cape, an Afrikaans speaking ‘plaas japie’ he learned to shoot and hunt from a very young age. He was the younger brother to “Bull” Malan and as a result had secondary opportunities prevalent to the times when the first born received academic and career preference.
He was also bullied at school, and in this he would forever forge a deep hatred for ‘bullies’ – he would always stand up for the ‘little guy’ and this would manifest itself in his convictions to battle against a ‘bully’ Nazi state as part of the Royal Air Force’s “Few”, a ‘no fear’ approach and he saw killing Nazi pilots and aircrew as necessary for the good of humankind. Later in life he also held no fear whatsoever of the National Party politician ‘bullies’ who had flirted with Nazism and saw them in the same light.
Named ‘Sailor’ after a stint in the Navy on the SATS General Botha and as a merchantman. He experienced the rise of authoritarianism in Germany in his frequent visits to Hamburg and Keil as a merchant sailor before 1939. Identifying Nazism as the enemy, he joined the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1940 in preparation for the war. His British loyalism and revulsion of fascism were also shared by his brother “Bull” Malan, who participated in the invasion of Madagascar in 1942 and later killed in action.
In his career as a naval merchantman, Sailor also becomes increasing exposed to various cultures and nationalities and takes on an embracing and tolerant view. During the Battle of Britain, the British relied on pilots from the Commonwealth to make up a critical pilot shortage and Sailor Malan was one of these pilots and with him came pilots from all over the world, of all colours and of all cultures (there was no such thing as a ‘colour bar’ in the Royal Air Force) – from commonwealth countries like India, Burma, Rhodesia, Jamaica, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and Canada, as well as pilots from Poland, France, Czechoslovakia and the USA. They made up almost one-third of the RAF pilots involved in the Battle of Britain – a demographic fundamentally different to the image so often created of these men as a bunch of tea drinking ‘tally-ho’ young white English.

Funnily, ‘Sailor’ would however develop a rather plummy English accent, and fellow pilots thought they were dealing with a English officer until they saw his ‘South Africa’ shoulder titles on his RAF uniform, his close fellow pilots would also nickname him ‘Hitler’ as a humorous take on his real first name, Adolph, however ‘Sailor’ as a nickname generally wins out and the name by which everyone gets to know him. However, it’s his combat record, coolness under fire, promotions and decorations alone are simply astonishing. To hear Sailor in his own words during the Battle of Britain, follow this link Sailor Malan; in his own words!
He first took part in evacuation of Dunkirk. During this battle he first exhibited his fearless and implacable fighting spirit. To demonstrate his nature, in one incident he was able to coolly change the light bulb in his gunsight while in combat and then quickly return to the fray.
When the Battle of Britain begun, 74 Squadron (known as ‘The Tigers’) was to take the full heat of the battle in what was known as ‘hell’s corner’ over Kent, the squadron was eventually based at the now famous ‘Biggin Hill’ aerodrome in the thick of the battle. Malan would famously develop “my ten rules of air fighting” which would change the RAF’s doctrine and contribute to Britains victory in the Battle of Britain – to read more on these rules, follow this link: ‘Ten of my rules for air fighting’ – Sailor Malan
Sailor Malan was given command of 74 Squadron, with the rank of Acting Squadron Leader at the height of the Battle of Britain on 8th August 1940. Three days later the Squadron was in battle. The day became forever known, “Sailor’s August the Eleventh”. The order was received at twenty minutes past seven to intercept a hostile raid approaching Dover. Little did the squadron know that they would participate in four separate air battles that day. When the Squadron returned to base after the fourth sortie, they had downed an astounding 38 enemy aircraft. Sailor Malan said later, in one of his masterly understatements:
“Thus ended a very successful morning of combat.”
Sailor Malan also worked on public relations to keep the British morale high. Here is a rare radio interview (follow Observation post link Sailor Malan – “in his own words”.
By D Day (i.e. Operation Overlord, the liberation of France and subsequently Western Europe), Sailor Malan was in command of 145 (Free French) Fighter Wing and was himself leading a section of the wing over the beaches during the landings in Normandy.
Sailor was a ruthless, skilful, and deadly hunter and killer, in all Sailor Malan scored 27 enemy aircraft kills, seven shared destroyed, three probably destroyed and 16 damaged. He was to receive the Distinguished Service Order decoration – not once, but twice and well as the Distinguished Flying Cross decoration, again not once – but twice. The Citations for the DSO’s and DFC’s say everything about his combat prowess and are worth a mention and a listing given their status:

Distinguished Service Order & Bar (DSO). In Sailor’s case the two DSO are awarded for bravery. Here are the citations;
Distinguished Service Order. Acting Squadron Leader Adolph Gysbert Malan, DFC (37604), Royal Air Force, No.74 Squadron. December 24th, 1940.
“This officer has commanded his squadron with outstanding success over an intensive period of air operations and, by his brilliant leadership, skill and determination has contributed to the success obtained. Since early in August 1940, the squadron has destroyed at least 84 enemy aircraft and damaged many more. Squadron Leader Malan has himself destroyed at least eighteen hostile aircraft and possibly another six.”
And on 22nd July, 1941:
Bar to the DSO. Acting Wing Commander Adolph Gysbert Malan, DSO, DFC (37604) Royal Air Force.
“This officer has displayed the greatest courage and disdain of the enemy whilst leading his Wing on numerous recent operations over Northern France. His cool judgement, exceptional determination and ability have enabled him to increase his confirmed victories over enemy aircraft from 19 to 28, in addition to a further 20 damaged and probably destroyed. His record and behaviour have earned for him the greatest admiration and devotion of his comrades in the Wing. During the past fortnight the Wing has scored heavily against the enemy with 42 hostile aircraft destroyed, a further 15 probably destroyed and 11 damaged.”
Distinguished Flying Cross & Bar. This this is still a ‘decoration’ and not a ‘medal’ so it’s very high on the senior level, and in Sailor’s case both times it is awarded for exceptional flying and bravery. Here are the citations for his Distinguished Flying Crosses;
Flight Lieutenant Adolph Gysbert Malan. (37604), Royal Air Force. June 11th, 1940.
“During May 1940, this officer has led his flight, and on certain occasions his squadron, on ten offensive patrols in Northern France. He has personally shot down two enemy aircraft and, probably, three others. Flight Lieutenant Malan has displayed great skill, courage and relentless determination in his attacks upon the enemy.”
Bar to the DFC. August 13th, 1940:
Flight Lieutenant Adolph Gysbert Malan. (37604), Royal Air Force.
“Since the end of May, 1940, this officer has continued to lead his flight and, on many occasions the squadron, in numerous successful engagements against the enemy. During the Dunkirk operations he shot down three enemy aircraft and assisted in destroying a further three. In June, 1940, during a night attack by enemy aircraft, he shot down two Heinkel 111’s. His magnificent leadership, skill and courage have been largely responsible for the many successes obtained by his squadron.”
British and Commonwealth Medals include:
- 1939-45 Star with Battle of Britain clasp
- The Air Crew Europe Star with France and Germany clasp
- The Defence Medal
- The War Medal (1939-1945) – with a mid Oak Leaf or MiD (Mentioned in Dispatches). The Oak Leaf on Sailor’s ribbon of this medal indicates the award of the King’s Commendation for Brave Conduct.
Foreign Decorations include:
- Legion of Honour (France) Officer Grade
- Croix de Guerre (France)
- Croix de guerre (Belgium) with bronze palm. The Bronze Palm means Sailor Malan was ‘Mentioned in Dispatches’ by the War Office specifically for a performing heroic or significant deed.
- Czecho-Slovakian Military Cross
To read more on Sailor Malan’s medals follow this link; Sailor’s medals
To understand Sailor Malan as a military leader, Bill Skinner DFC, with whom Sailor often flew, summed up Sailor Malan very well when he said of him:
“He was a born leader and natural pilot of the first order. Complete absence of balderdash. As far as he was concerned, you either did your job properly, or you were on your way. He inspired his air crews by his dynamic and forceful personality, and by the fact that he set such a high standard in his flying.”
Sailor Malan was one of the most outstanding British Fighter Command’s fighter pilots of the 1939-45 war, by the end of 1941 was the top scorer – a record which he held for three years. But he was much more than an individual performer. He remains one of the highest scoring fighter aces to have served with Fighter Command and one of The Few as described by Sir Winston Churchill, who also incidentally became Godfather to Sailor’s new-born son – Jonathan Malan. He had assimilated the fierce and fanatical “tiger spirit” of his squadron, and this ‘Sky Tiger’ spirit he inspired in others and in so carried the Squadron to its great deeds. He literally lived and breathed the squadron’s motto – I fear no man.
The Battle of Britain and D Day moulded Sailor Malan as a champion for freedom, he simply held the view that shooting down Nazi aircraft was good for humanity, and this fearlessness translated into his personal politics. Sailor Malan left the Royal Air Force and returned to South Africa in 1946. He joined Anglo American as Harry Oppenheimer’s personal secretary, and later it was Oppenheimer who would turn to Sailor Malan as the best candidate, given his exemplary war record, his liberal disposition, leadership and likeable personality – to lead The War Veterans Action Committee as its President.
In Sailor Malan’s own words, he would sum up his intentions and what the WVAC and The Torch Commando was all about – of its primary mission, he said:
“The Torch Commando was established to oppose the police state, abuse of state power, censorship, racism, the removal of the coloured vote and other oppressive manifestations of the creeping fascism of the National Party regime”.
Opening Shots
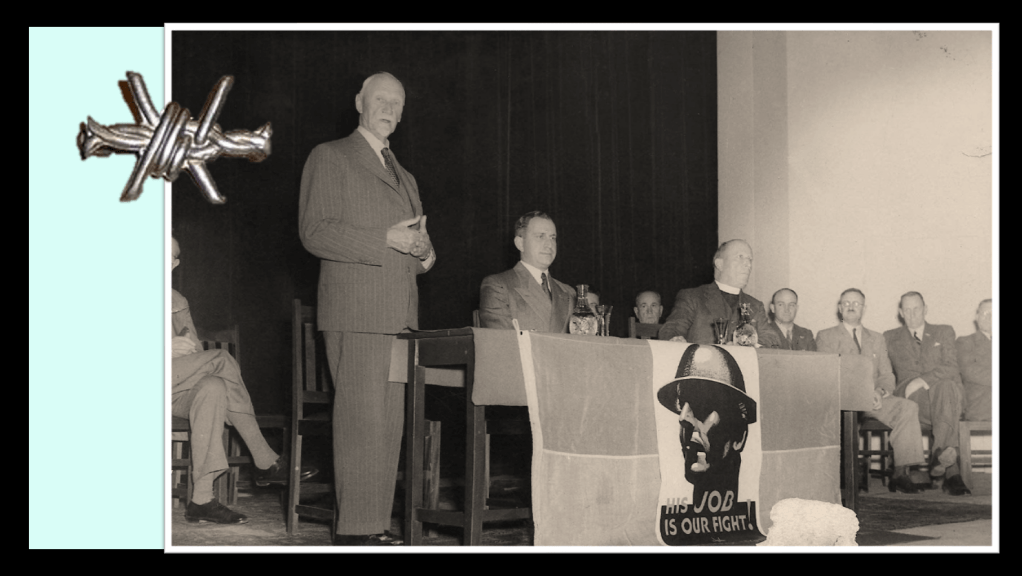
The opening protest by the WVAC started on a relatively small scale, on the 21st April 1951 at the cenotaph near the Johannesburg City Hall commemorating soldiers who had died in World War 1 and World War 2. The WVAC ex-servicemen present, in protest against the advent of National Party’s Apartheid policies pledged themselves to defend the values for which their comrades had died, and to demonstrate their intention they draped a coffin in the National Flag to symbolize the death of the South African constitution and placed a placard to that effect.
The ’constitutional crisis’ they referred to on the plagued is the opening shot of the National Party to implement their barrage of ‘Grand Apartheid’ laws, the crisis began earlier in 1951 when the National Party announced proposed legislation called the ‘Separate Representation Act’ to remove so-called ‘Coloureds’ from the Common Voters Roll – correctly this incorporated all franchise qualified ‘Black’ and ‘Coloured’ voters in the Western Cape – known as the Cape Franchise, in essence ‘Coloureds’ and Whites were on the same voters roll since the abolishment of slavery and ‘apprenticeships’ from 1853. To change the constitution required a 2/3 majority of MP’s at a joint sitting of both Houses of Parliament (National Assembly and the Senate).
The constitution of the Union of South Africa was rock solid to prevent right wing racial politics of the old Boer Republics of the Transvaal and Orange Free State from interfering with it. To many white South Africans this part of the Union’s Constitution was a “solemn compact” at the very core of the Union – legally and morally binding and for the time being the Cape Franchise kept an uneasy peace on issues relating ‘black’ political emancipation.
The National Party did not have the required majority by way of popular vote. However, they had a plan, they were to gerrymander, load the Senate with new National Party seats and pass legislation to get their majority and push their legislation through.
The Separate Representation Act caused significant outrage – the war veteran’s concern was that removing Coloureds from the voters roll, as they constituted a significant voting bloc, would pave the way for future and more sinister racially based Apartheid legislation, the complete marginalisation of ‘black’ political representation and a break-up of the Union’s constitution to form a ‘white Afrikaner’ Republic and breaking the ‘Union’ and British Dominion status on a ‘whites-only’ voting ticket.
The Torch Commando – next instalment
What follows next is called ‘The Steel Commando’ – please click through to this Observation Post link which covers this phase in depth.
The Torch Commando – Part 3, The Steel Commando
Written and Researched by Peter Dickens
References
South African History Association (on-line) ‘Tracing the unbreakable thread’
Military History Journal , Vol 5 No 5 – June 1982, Flying High: The Story of the Women’s Auxiliary Air Force 1939-1945. By Major Marjorie Egerton Bird and Molly Botes
The Torch Commando & The Politics of White Opposition. South Africa 1951-1953, a Seminar Paper submission to Wits University – 1976 by Michael Fridjhon.
The South African Parliamentary Opposition 1948 – 1953, a Doctorate submission to Natal University – 1989 by William Barry White.
The influence of Second World War military service on prominent White South African veterans in opposition politics 1939 – 1961. A Masters submission to Stellenbosch University – 2021 by Graeme Wesley Plint
The Rise and Fall of The Torch Commando – Politicsweb 2018 by John Kane-Berman
The White Armed Struggle against Apartheid – a Seminar Paper submission to The South African Military History Society – 10th Oct 2019 by Peter Dickens
Not for ourselves – a history of the South African Legion by Arthur Blake
Sailor Malan fights his greatest Battle: Albert Flick 1952.
Sailor Malan – By Oliver Walker 1953.
Lazerson, Whites in the Struggle Against Apartheid.
The White Tribe of Africa: 1981: By David Harrison
Ordinary Springboks: White Servicemen and Social Justice in South Africa, 1939-1961. By Neil Roos.
Sailor Malan fights his greatest Battle: By Albert Flick 1952.
Kimberley Calls and Recalls. Life Magazine, 25 June 1951.
Related Work
Torch Commando – Steel Commando The Steel Commando
Truth Legion A search for the … Truth … Legion!
Torch Commando – ‘New’ rare footage of The Torch Commando in action, the first mass protests against Apartheid by WW2 veterans.
Sailor Malan ‘Freedom Fighter’ Sailor Malan; Fighter Ace & Freedom Fighter!
Sailor Malan – rules of air fighting ‘Ten of my rules for air fighting’ – Sailor Malan
Sailor Malan Sailor’s medals
The Torch Commando Series
The Smoking Gun of the White Struggle against Apartheid!
The Observation Post published 5 articles on the The Torch Commando outlining the history of the movement, this was done ahead of the 60th anniversary of the death of Sailor Malan and Yvonne Malan’ commemorative lecture on him “I fear no man”. To easily access all the key links and the respective content here they are in sequence.
In part 1, we outlined the Nazification of the Afrikaner right prior to and during World War 2 and their ascent to power in a shock election win in 1948 as the Afrikaner National Party – creating the groundswell of indignation and protest from the returning war veterans, whose entire raison d’etre for going to war was to get rid of Nazism.
For the in-depth article follow this link: The Nazification of the Afrikaner Right
In part 2, in response to National Party’s plans to amend the constitution to make way for Apartheid legislation, we outlined the political nature of the military veterans’ associations and parties and the formation of the War Veterans Action Committee (WVAC) under the leadership of Battle of Britain hero – Group Captain Sailor Malan in opposition to it. Essentially bringing together firebrand Springbok Legionnaires and the United Party’s military veteran leaders into a moderate and centre-line steering committee with broad popular appeal across the entire veteran voting bloc.
For the in-depth article follow this link: The War Veterans’ Action Committee
In Part 3, we cover the opening salvo of WVAC in a protest in April 1951 at the War Cenotaph in Johannesburg followed by the ratification of four demands at two mass rallies in May 1951. They take these demands to Nationalists in Parliament in a ‘Steel Commando’ convoy converging on Cape Town. Led by Group Captain Sailor Malan and another Afrikaner – Commandant Dolf de la Rey, a South African War (1899-1902) veteran of high standing their purpose is to raise support from Afrikaner and English veterans alike and they converge with a ‘Torchlight’ rally of 60,000 protestors and hand their demands to parliament.
For the in-depth article follow this link: The Steel Commando
In Part 4, in response to the success of The Steel Commando Cape Town protest, we then look at the rise of the Torch Commando as South Africa’s largest and most significant mass protest movement in the early 1950’s pre-dating the ANC’s defiance campaign. Political dynamics within the Torch see its loyalties stretched across the South African opposition politics landscape, the Torch eventually aiding the United Party’s (UP) grassroots campaigning whilst at the same time caught up in Federal breakaway parties and the Natal issue. The introduction of the ‘Swart Bills’ in addition to ‘coloured vote constitutional crisis’ going ahead despite ineffectual protests causes a crisis within the Torch. This and the UP’s losses in by-elections in the lead up to and the 1953 General Election itself spurs the eventual demise of The Torch Commando.
For the in-depth article follow this link: The ‘Rise and Fall’ of the Torch Commando
In Part 5, we conclude the Series on The Torch Commando with ‘The Smoking Gun’. The Smoking Gun traces what the Torch Commando members do after the movement collapses, significantly two political parties spin out the Torch Commando – the Liberal Party of South Africa and the Union Federal Party. The Torch also significantly impacts the United Party and the formation of the breakaway Progressive Party who embark on formal party political resistance to Apartheid and are the precursor of the modern day Democratic Alliance. The Torch’s Communists party members take a leading role in the ANC’s armed wing MK, and the Torch’s liberals spin off the NCL and ARM armed resistance movements from the Liberal Party. We conclude with CODESA.
For an in-depth article follow this link: The Smoking Gun



Pingback: The Nazification of the Afrikaner Right | The Observation Post
Excellent article which deserves a wide audience. Thank you.
LikeLike
Pingback: The ‘Rise and Fall’ of the Torch Commando | The Observation Post
Pingback: The Smoking Gun | The Observation Post
Pingback: The Steel Commando | The Observation Post
Pingback: The Torch Commando | The Observation Post