So, talking Olympics, but in a military context, who are South Africa’s greatest medalists?
Unfortunately we have to separate this into two sub categories as the National Party in 1948 decided that anyone fighting for the Allies under the banner of the “South African Union” was somehow “British” (so too their medals – the “Commonwealth” bit to these decorations mattered not a jot to the Nats) and anyone fighting for the ‘White’ Apartheid Republic they brought about in 1961 was somehow more “South African” – and they created a whole new set of medals in paramount to the “British and Commonwealth” ones – declaring these as “foreign” medals – which meant a simple peacetime SADF ’Skiet medal” (shooting proficiency medal) would be more senior than a Commonwealth decoration for wartime gallantry.
Naturally this caused a lot of distress for our WW1 and WW2 veterans at the time, some refusing to allow basic service medals to precede their hard earned combat medals – and it also caused lots of confusion. True, the Nationalists had to change them as South Africa was kicked out/left the British Commonwealth, no choice – but they did not have be sinister and give paramountcy over the Commonwealth medals.
Adding to this confusion is the current ANC dispensation who took the position in 2003 that medals awarded by the Apartheid Republic were for “Aparthied soldiers” and they created a whole new set to replace them for SANDF soldiers of a “democratic” South Africa – one thing they did right is they did not make them “paramount” to the SADF medals which maintain seniority (which the Nats did not do). To say this is a messy subject would be an understatement.
We also need to understand who is the South African with the “most” medals – like an Olympian who has won the most medals of any category – Gold, Silver or Bronze as opposed to the South African who has won the most “highest” medals for gallantry- again like an Olympian who has won the most “gold” medals.
Now to announce the winners:
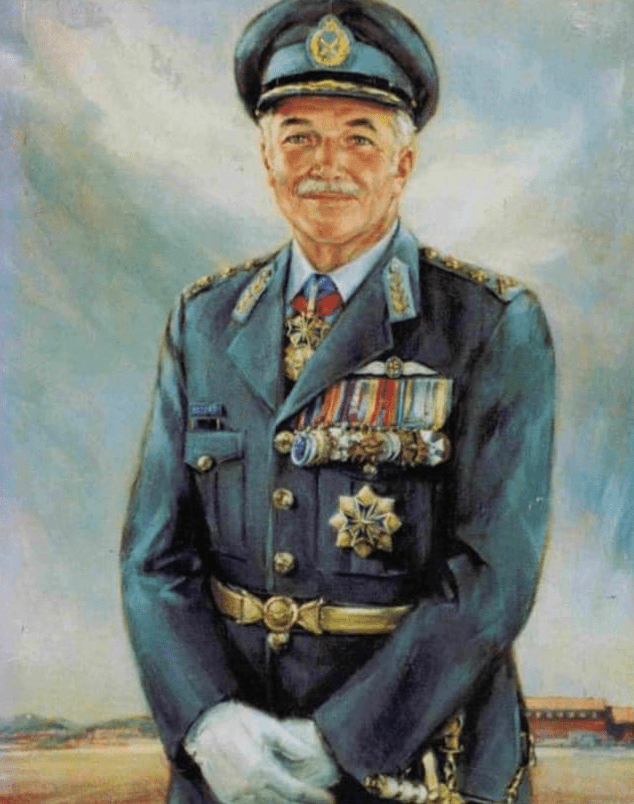
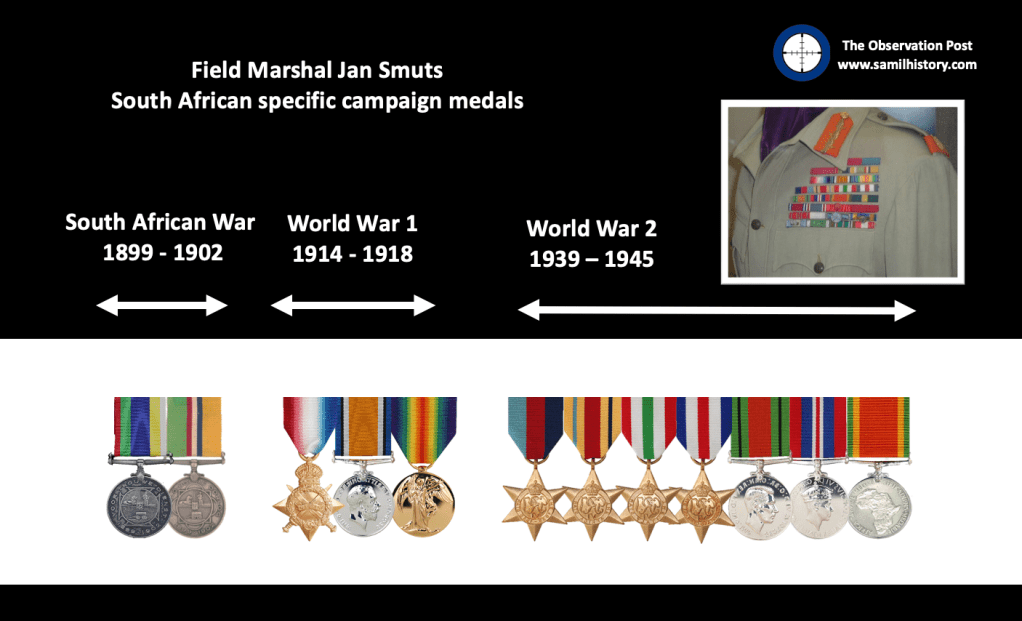
The winner of the “most” medals i.e. the most decorated South African of the “Union” period is ….. Field Marshal Jan Smuts – here’s his rack:
Field Marshal Jan Christian Smuts OM,CH,DTD,ED,PC,KC,FRS
- Order of Merit (OM) – British and Commonwealth (WW2)
- Order of the Companions of Honour (CH) – British and Commonwealth (WW1)
- Dekoratie voor trouwe Dienst (DTD) – ZAR Republic (Boer War 2)
- Efficiency Decoration (ED) – South Africa (Interwar and WW2)
- Privy Council (PC) – British and Commonwealth
- King’s Counsel (KC) – a legal appointment post nominal
- Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS)
- Bencher of the Middle Temple – a legal appointment
- South African Republic and OFS War Medal – ZAR Republic (Boer War 2)
- 1914/15 Star (WW1)
- British War Medal 1914 – 1918 (WW1)
- Victory Medal (WW1)
- General Service Medal
- King George V’s Jubilee Medal – 1935
- King George VI’s Coronation Medal – 1937
- 1939 – 1945 Star (WW2)
- Africa Star (WW2)
- Italy Star (WW2)
- France and Germany Star (WW2)
- Defence Medal 1939 – 1945 (WW2)
- War Medal 1939 – 1945 (WW2)
- Africa Service Medal 1939 – 1945 (WW2)
- Order of Merit (U.S.A.)
- EAME Campaign Medal – U.S.A.(WW2)
- Order of the Tower and Sword for Valour, Loyalty and Merit (Portugal)
- Grootkruis van die Orde van de Nederlandsche Leeuw – Netherlands (WW2)
- Grand Cordon of the Order of Mohamed Ali (Egypt)
- Grand Cross of the Order of the Redeemer – Greece (WW2)
- Grand Cross of the Order of Léopold II – Belgium (WW2)
- Croix de guerre – Belgium (WW1)
- Légion d’honneur Croix de Commandeur – France (WW1)
- La Grand Croix de l’Ordre de L’Etoile Africane Ster – Belgium (WW2)
- King Christian X Frihedsmedaille ‘Pro Dania’ – Denmark (WW2)
- Aristion Andrias Gold Cross – Greece (WW2)
- Albert Medal of the Royal Society of Arts
- Woodrow Wilson Peace Medal1
36 Total
Smuts is unique in the sense that his two Boer War Republican medals pre-date his Union medals.
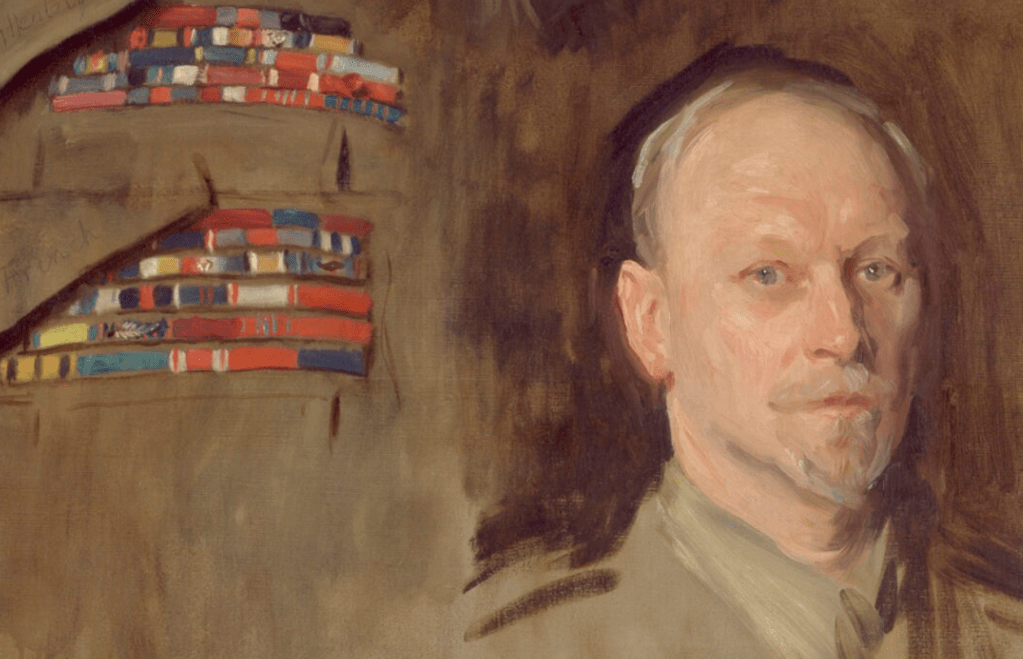

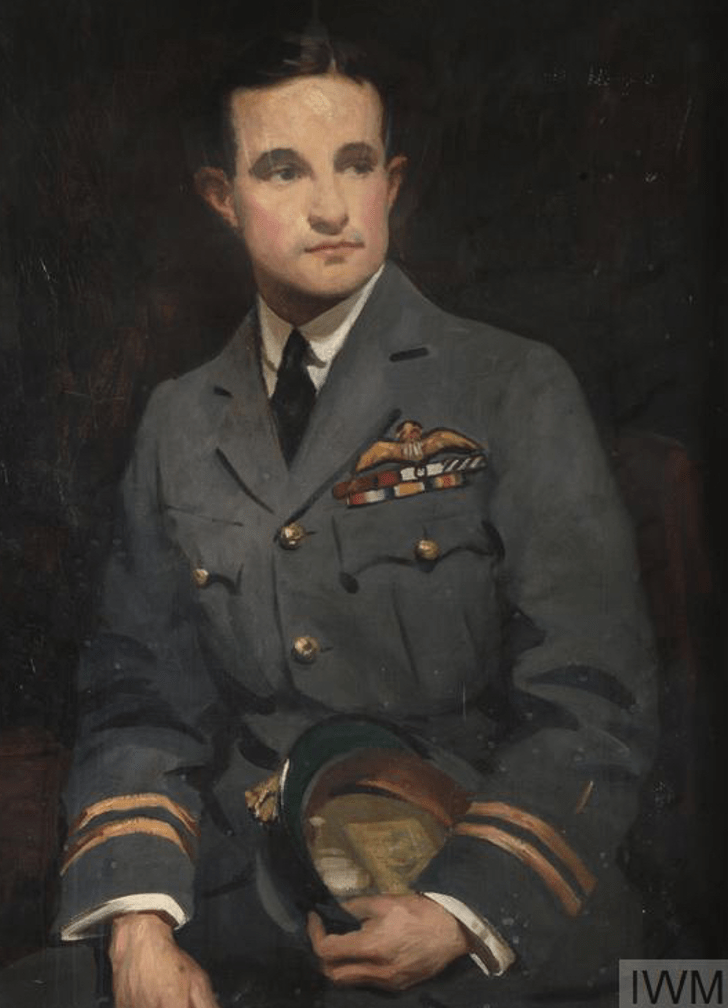
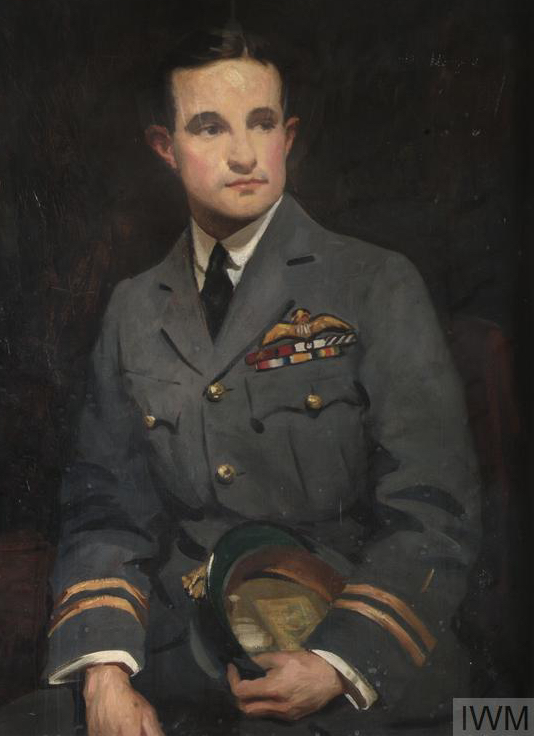
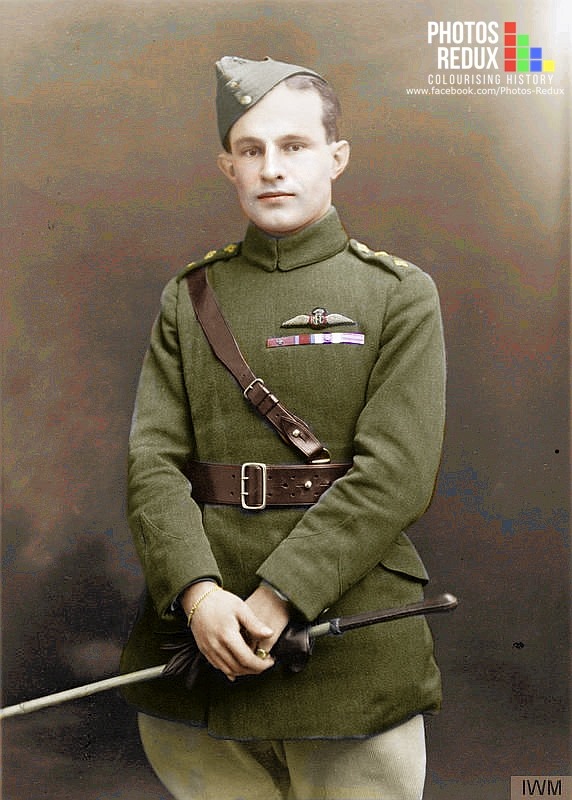
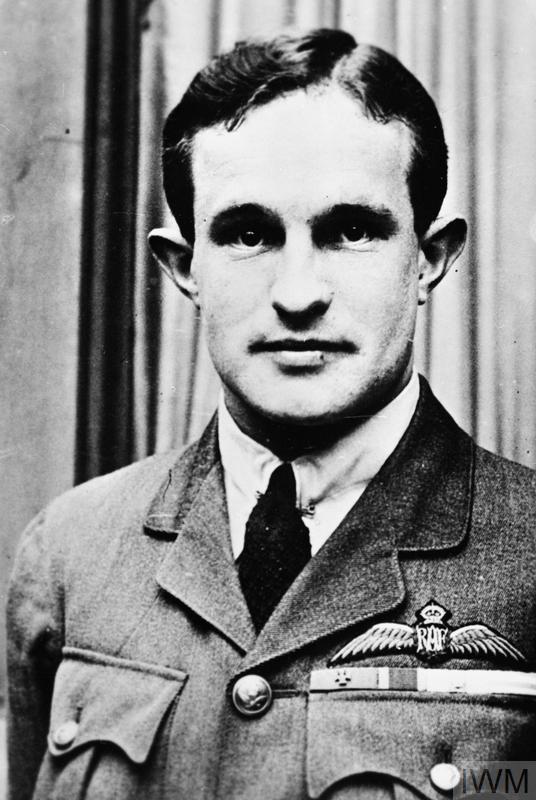
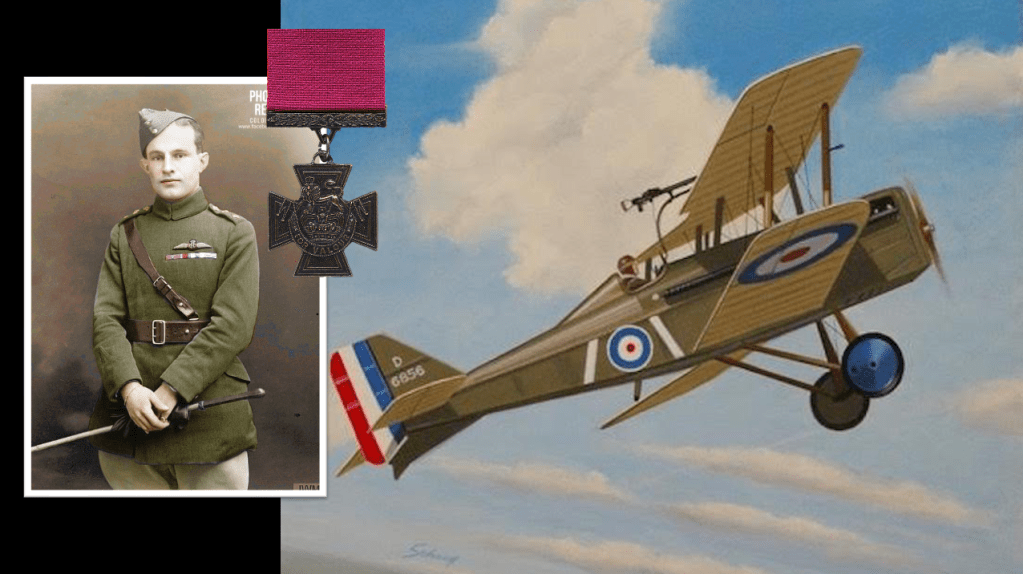
The winner of the “highest” medals i.e. the highest decorated South African of the “Union” period is …. Captain Andrew Beauchamp-Proctor – here is his rack:
Captain Andrew Beauchamp-Proctor VC,DSO,MC&Bar,DFC
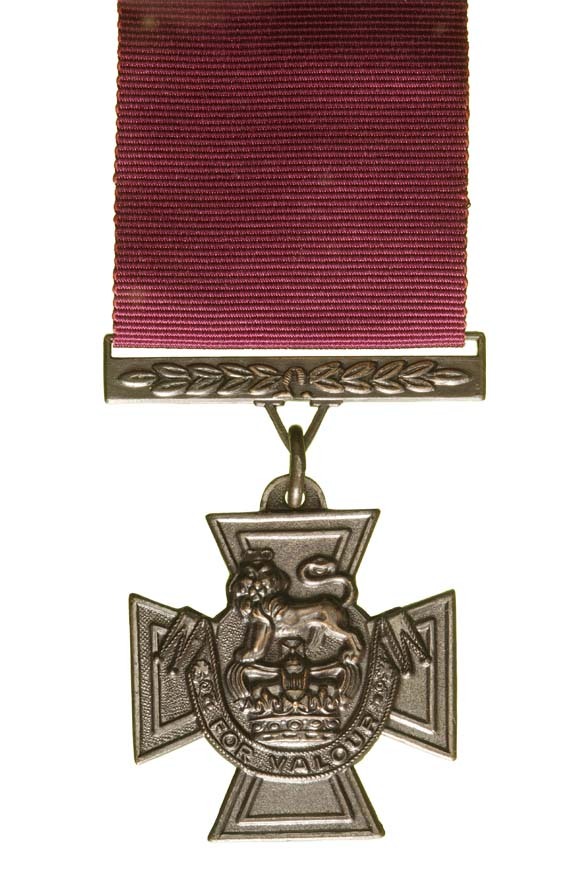
- Victoria Cross (WW1)
- Distinguished Service Order (WW1)
- Military Cross and Bar (WW1)
- Distinguished Flying Cross (WW1)
- 1914 – 1915 Star (WW1)
- British War Medal (WW1)
- The Victory Medal (WW1)
Captain Beauchamp-Proctor is not unique in the sense that all his highest medals were earned whilst fighting in British military constructs as a South African Union citizen – which was perfectly acceptable then.
The South African winner of the “most decorated” South African in the “South African Republic” SADF period is ….. General Bob Rogers – here is his rack:
General Bob Rogers SSA, SM, MMM, DSO, DFC&Bar
- Star of South Africa (SSA) (South Africa)
- Southern Cross Medal (SM) (South Africa)
- Military Merit Medal (MMM) (South Africa)
- Korea Medal (South Africa)
- Pro Patria Medal (South Africa)
- Good Service Medal, Gold (30 Years – South Africa)
- Good Service Medal, Silver (20 Years – South Africa)
- Union Medal (South Africa)
- Distinguished Service Order (DSO) (WW2)
- Distinguished Flying Cross and Bar (DFC and Bar) (WW2)
- 1939–45 Star (WW2)
- Africa Star (WW2)
- Italy Star (WW2)
- War Medal 1939–1945 – Mentioned in Dispatches (WW2)
- Africa Service Medal (WW2)
- Distinguished Flying Cross (USA)*
- Air Medal Bronze with Oak Leaf Cluster (USA)*
- Order of Military Merit (Korea) (Chungmu cordon) with Gold Star
- United Nations Service Medal for Korea
- Korean War Service Medal
- Grand Star of Military Merit (Chile)
- Army PUC Presidential Unit Citation (USA)*
*American awards issued to 2 SAAF Squadron members under their command in the Korean War.2
23 Total
Note: General Rogers’ medal set are a combination of SADF (Republican) and UDF (Union) medals and decorations, and like Smuts some foreign ones too.
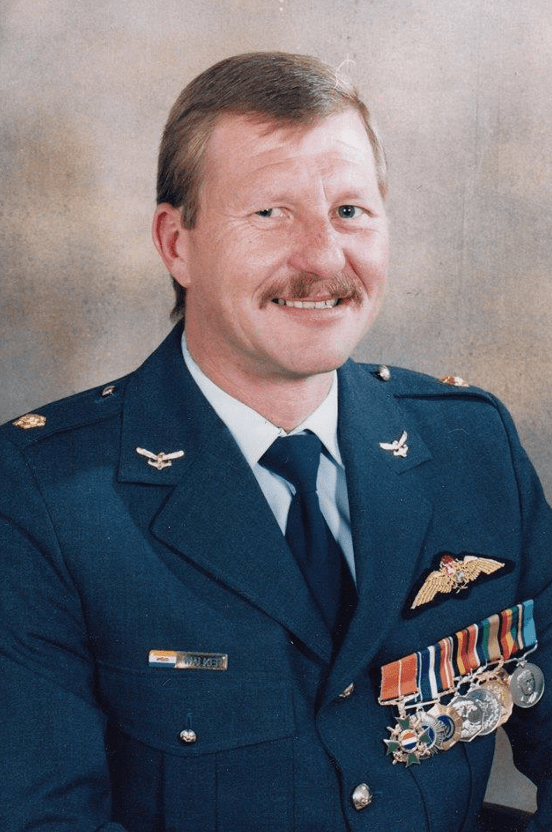
The winner of the “highest decorated” South African in the SADF “Republic” period is …. Major Arthur Walker – here is his rack:
Major Murray Walker HCG&Bar, SM
- Honoris Crux (Gold and Bar) – South Africa
- Southern Cross Medal – South Africa
- Pro Patria Medal – South Africa
- Southern African Medal – South Africa
- General Service Medal – South Africa
- Good Service Medal Bronze – South Africa
- Zimbabwean Independence Medal 1980 – Zimbabwe
- General Service Medal – Rhodesia
- United Nations Medal (Mozambique – United Nations)
Major Walker is unique in that won the Honoris Crux Gold (HCG) twice – the only South African to have a “Bar” to a HCG.
Overall Winning Medalists
So, of these four great medalists – who are the winners of the “most” and the “highest” given the grade and total sweep of the medals on offer – the answer:
Field Marshal Jan Smuts is the overall winner of the “most decorated South African”.
Simply because he has more decorations and medals (36) than Bob Rogers (23).
Andrew Beauchamp-Proctor is the overall winner of the “highest decorated South African”.
Simply because he has a Victoria Cross (VC) and his raft of decorations for gallantry serve to qualify it further – his DSO, two MC and DFC, putting him ahead of the other South African VC recipients – the highest gallantry award for the SADF was the “diamond” Honoris Crux (HCD), it was meant to be on the same level as a VC (albeit not the same as the VC is a stand alone, there is graded degree of bravery as there is with a HC set)- and nobody ever received a “diamond” Honoris Crux (HCD) in any event, it was never awarded, and no one ever will, it has been discontinued.
Of the new SANDF “Highest” decoration is the Nkwe ya Gauta – Golden Leopard – it replaced the Gold Honoris Crux (HCG) and like the HC set it is part of graded gallantry decorations going up in importance and there is no “diamond” Leopard – whereas the Victoria Cross is still a stand alone decoration and has no equivalent – so Beauchamp-Proctor still remains the “highest” decorated – and will remain such well into our living memory. So far there have been 3 recipients of the Nkwe ya Gauta – Golden Leopard – all of them posthumous.
Please note this is not meant to degrade any one over the other – all four of these men are great South Africans.
Written and Researched by Peter Dickens