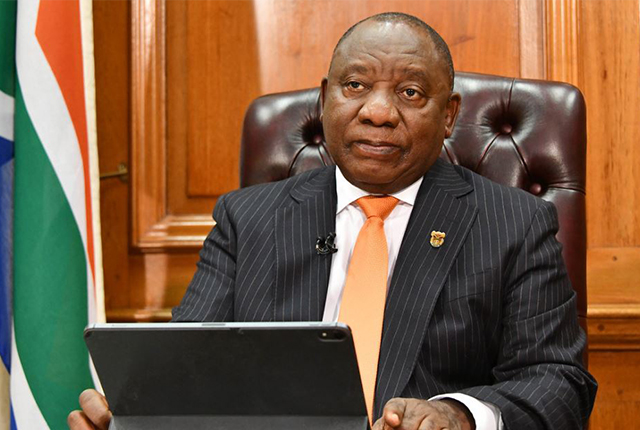
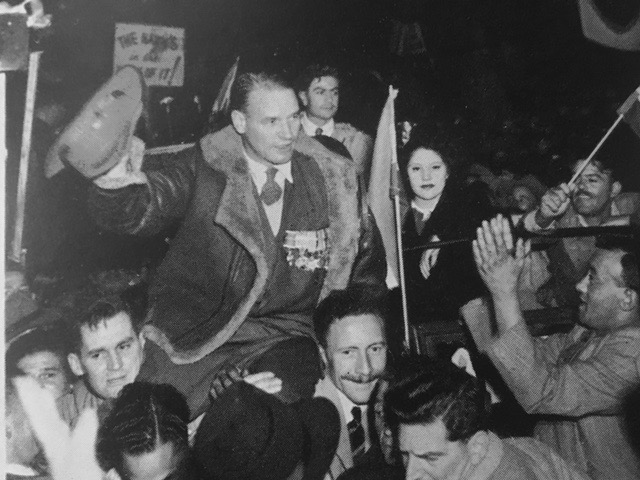Sitting here in 2023 listening to yet another Nationalist, this time an African Nationalist President urging a Constitutional workshop to forward Nationalistic aims of land appropriation and ‘economic transformation’ in the guise of building a national ‘rainbow’ identity to redress the past, to pass off his own parties political inadequacies and flaws as been a ‘constitutional’ right to fight the wrongs committed “on the many” by what he termed “the state that came before us”.
Typical, comes the universal cry, the ANC playing the ‘Apartheid’ card yet again, corrupt as ever now even trying to manipulate the constitution for their own duplicitous aims. Our beloved and hard fought South African Republic becoming like the Republic of Zimbabwe, another ‘Banana Republic’.
The ‘politics of pain’ rearing its political head, the ‘race card’ played again and again – however playing the race card is nothing new to Nationalists, it has been played for many decades by any ‘nation’ seeking freedom and ‘identity’– and herein lies a deep irony when it comes to creating Republics out of the ideology of singular ‘nationhood’ – there is always another ‘race’ to blame for it – a license to target another national group as the origins of all their economic, social and political woes.
Even President Ramaposha did not shy away from it one bit – the ‘state before’ his (i.e., the Old National Party ‘Apartheid’ Republic) excelled in it, the idea that a ‘wounded’ nation, dealt a terrible misdeed, must for the survival of its identity and ‘nationhood’ oppress other nationalities/cultures/languages and even entire nation states.
Republic to Union and back again!
As military veterans we stand by our hard-fought freedoms, from those who fought the ‘cold’ war of communism versus capitalism, and those of us who served to see the country through transition to an all embracing democracy. We all covet the ideals of freedoms so protected in our Republic’s constitution – it came with a lot of blood and toil.
To see clearly how these ideals of a ‘Democratically Free Republic’ are transitioning to a ‘Banana Republic’ as all the government owned and run utilities and the SANDF, slowly collapses around us is distressing. The fear of another ‘Zimbabwe’ looming large as Eskom turns the country’s economy on and off.
So, how did South Africa go from its lofty ideals of a Union, a ‘federation of states and nations’ in 1910, to a Banana Republic? Intriguing question and it has to do with the old argument between British Imperialists and Boer Imperialists as to under whose ‘influence’ Southern Africa should be managed (only if it was ‘European’ civilisation leading it mind) – an argument with started long before The South African War (1899-1902) and one that leads directly to the Union of South Africa and it is one which eventually leads to the formation of the Republic of South Africa – as the likes of two Afrikaners, Jan Smuts and D.F. Malan would go hammer and tongs at each other over the issue for decades.
The white Afrikaner Nationalist right wing and their continued obsession with creating a Afrikaner led Republic from the “Limpopo to the Cape”, and the white English and many moderate white Afrikaners happy with a ‘Union’ along Federal lines of all states in Southern Africa (Colonial, Protectorate and Republic) with British Dominion oversight – like Australia and Canada. The net outcome of it all today – the fully democratic Republic of South Africa – or ‘Banana Republic’ as it is sarcastically referred to, ironically by these same white Republicans and Unionists, who either inadvertently or even directly created it for themselves.
Written as far back as 1900 by Leo Amery, in the middle of the South African War (1899-1902) in his History of the Boer War, was this completely differing outlook, those of the Unionists and those of the Republicans and it is clearly mapped out. It’s very insightful for the time. Here it is:
“Those who believe in progress, in honest government, in political liberty and equality, must upon true statement of the facts, be on the side of England. Those to whom nationalism is all in all, who hold the creation of a nation state, with racial and linguistic characteristics of its own, is the one supreme object of political development – an object justifying every means for its attainment – will naturally be on the side of the Afrikaner Republics.”
Please note: By 1900, Britain regarded itself as a Constitutional Monarchy (where Parliament and Royalty for all intents and purposes of actual governance – are separate) and Parliament considered a ‘Liberal Democracy’ – a tussle between ‘Whigs’ (Liberals) and ‘Tories’ (Conservatives) with a ‘human rights’ agenda (equality and suffrage), secular in nature and with an acculturation focus i.e., getting various cultural groupings to adopt British values and governing principles as their own, whilst at the same time keeping their cultural identity and individual liberties – even in the context of Empire, that was (and remains) the basis of Britain’s Parliamentary system and it needs to read into the context of its time in history and the franchise – which believe it or not was ‘multi-cultural’ and ‘qualified’ – even for 1900. Funnily, the same philosophy even exists to this day, in essence it has not changed.
Also please note: The Boer Republics at the time were regarded Nationalist Republics run entirely opposite to the British, they were seen as ‘oligarchies’ or even as devolved ‘theocracies’ (not secular at all – State and Church are linked) whose focus was on cultural prejudice (not acculturation in any real respect) i.e., ‘them and us’ and a complete separation of Boer values from all others, almost a cultural assimilation of imposition – and in so combining their ‘Nationalism’ and ‘identity’ into a unilateral ‘nation state’. This manifested itself in the Boer Republic’s Parliamentary systems and needs to be read into the context of its time in history and the franchise as well (which at the time was exclusively ‘Boer’ and ‘white’). Funnily, the same philosophy resurfaced in 1961 when the whole of the Union of South Africa declared itself a Republic.
Obsessing over Republics
So, what’s with the ‘Boer’ obsession with the ideals of Republics and the idea of Boers tacking their identity to them – sheer nationalism?
As far back as South Africa’s initial colonisation goes, Republican ideology has accompanied it. It starts with the Dutch East India Company (VOC) in the Cape Colony with the establishment of ‘Free Burghers’ – these ‘Free Burgers’ held their freedom as paramount, many of them escaping religious and nationality persecution in Europe. The Cape Colony fell under a Dutch Republic government with the VOC as an administrator and the ‘Free Burgher’ colonies fell under it, this Dutch Republic was later replaced by a French Republic vassal state called the Batavian Republic.
Contrary to a mainstream belief, these ‘Free Burghers’ and their fierce need for independence from a meddling state would not start with the British, it would start with the Dutch! .. Huh, how so? Well, here’s some little known history not usually found in a school history book ..
By 1795, dissatisfaction with the Dutch East India Company caused the Free Burghers of Swellendam to declare their own Republic, and Hermanus Steyn its President of the ‘Republic of Swellendam’. It lasted until the 1st British occupation of the Cape. Not just The Republic of Swellendam, the Free Burghers of Graaf-Reinet, also in 1795, had issues with the Dutch East India Company on policies regarding the frontier and tax, and they too declared the Republic of Graaf-Reinet, it also lasted until the 1st British occupation of the Cape in its war against the French.
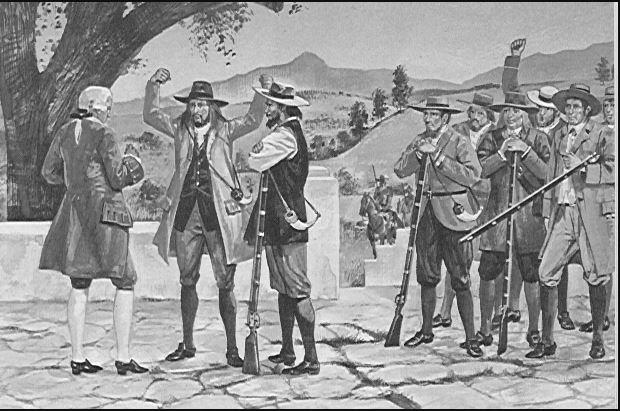
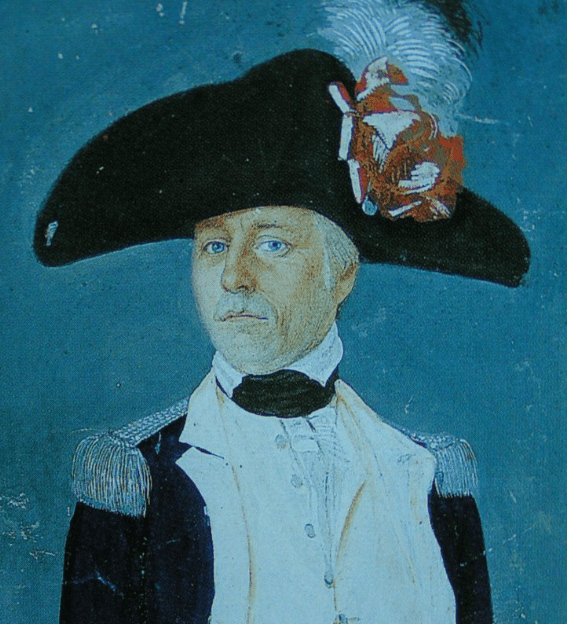


Images: The declaration of the Republic of Swellendam, and Southern Africa’s first real President, President Hermanus Steyn of the Republic of Swellendam 1795.
The 2nd British occupation of the Cape after the defeat of the Batavian Republic and the French Republic brought with it policies some of the Dutch speaking Burghers could not abide by. The British had been protecting the Dutch aristocracy during their Napoleonic and Batavian exile – after the Battle of Waterloo in 1815 finally settled the matter, the Dutch sold their Cape Colony to the British to aid in the re-establishment of their country (£6,000,000 then, now worth £150,000,000 or ZAR 3,380,000,000 – more or less). So here’s another inconvenient truth, the British did not ‘steal’ the Cape Colony from the Dutch, the Dutch sold it fair and square to the British to help them re-build the Netherlands after the Napoleonic wars.
The British outlook on suffrage as opposed to the Dutch one would clash in their new colony from the get go. Dissatisfaction started when the British banned Dutch slave traders from entering any Cape port from 15th June 1814, squeezing labour supply, then the British announced the abolition of slavery completely in 1834, they also announced a universal qualified franchise vote putting some ex-slaves and black citizens on the same footing as some white ones.
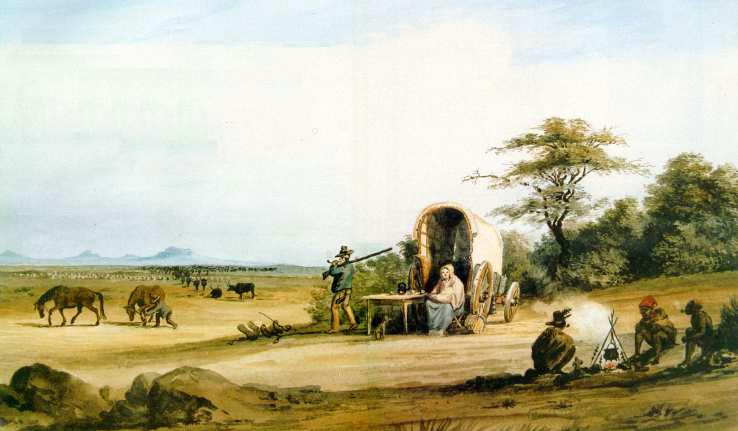
To top this indignity to the Burghers, the British announced English as the only official language in the Cape Colony and issued terms for the compensation of slaves which were viewed as unacceptable. Burghers had to go to Britain to get their compensation, an impossibility for many slave owners on the frontiers especially – and the amount been compensated was deemed as way under-valued in any event. With this indignity, and with their fierce need for independence – language, identity and religion, some Cape Burghers on the far-flung Colony’s frontiers (estimated at only 7.8% of the total population) upped sticks a year later in 1835 in a “Great” Trek to form a whole bunch of new Republics north of the Cape Colony’s border.
Consider why a Republic, Republics by now are based on their lofty French Republic ideals of Liberty, Equality and Fraternity are highly appealing to anyone seeking ‘Freedom’, they also should be free of domination and oversight (theoretically) by other states, and for a people seeking a separate national identity and nation state this is very appealing. But and it’s a BIG BUT, the types of Republics these Burghers were seeking to establish would manifest a version of racial servitude taken with them, strict in Calvinism and steeped in the Old Testament these ‘Burghers’ saw themselves as God’s ‘Chosen People’ in Africa – a superior race, certainly to their slaves and local African inhabitants, which they simply dismissed as “Kafir” (an Arabic term adopted from Muslim slaves and banished exiles from the Dutch East Indies) meaning “heathens” and therefore unworthy under God – the idea the hated British came up with – that slaves and heathens could hold the same rights as them in future – was an abhorrent one – and herein would lie a future problem (and future derogatory term).
A heady concoction of the ideals Liberty, Equality and Fraternity – but only for the white ‘Free-Burgher’ Nation – within their strong confines of identity, and one in which the ‘servitude’ of other racial groups played a key role – they would have to either barter or shoot their way in to gain land to establish Republics, and they did both. They would also need a disenfranchised labour class to work the vast tracks of arid farmland or in household servitude, they would source this labour either locally when they got there, primarily through a old Dutch/VOC indentured slavery system called the “inboekstelsel” system or take labour and servants with them – and they did both.
It is estimated in some historical sources that the ratio of Voortrekker/Trek Boer to Servant/Labour taken with them from the Cape Colony commencing in 1835 was as much as 1:1. This ratio is easily seen in this sad statistic, of the recorded 282 white Voortrekkers killed along the Bloukrans during the Zulu attacks of the 16th and 17th February 1838, there are 250 ‘black’ servants also recorded as killed by the Zulu’s in addition to their white benefactors. A homogeneous trek of white trekkers the Great Trek was not.
The inboekselings system was widely used by the Boers in the region that would ultimately comprise the Transvaal, the system had its origins in driving Khoi-Khoi to labour in the Cape by the Dutch/VOC, and was still in use by the Batavian Republic (French) when they controlled the Cape. It was a system of ‘indentured slavery’ (indentured or contracted labour with limited or no rights) – primarily of Black women and children captured by force and indentured to their Boer masters till 25 years of age for the men and 21 years of age for women, it also formed a lucrative trade for struggling farmers on the frontiers of the Transvaal known as ‘Black Gold’. It is also not a ‘tiny’ or isolated affair, as numbers go, Keith Breckenridge in ‘his work ‘power without knowledge’ estimates the ratio between inboekstelsel labour and white Voortrekker by 1866 as 1:10 (10% of the population).

In either event – and another inconvenient truth, between the labour taken with them by the Boer trekkers and the labour acquired when they got to their destinations, within all the future Republics declared by the trekking Boers, there would exist from the very beginning a very large class of displaced black servants and indentured black labourers who were given no rights whatsoever – no right to own land, no right to political representation and no suffrage whatsoever. Most inboekselings remained with the farmers after their indenture period terminated as employed farm labour and servants and in this way the Boer Republican governments also sought to create a ‘black’ buffer class between themselves and the tribal Africans. They would exist on Boer farms in separated conditions in their ‘kraal’ – a very large separated sub-class and disenfranchised social construct which would remain with the Afrikaner communities for nearly two centuries and one that can still be seen in rural areas to this day.
The British, as a world Super-power at this time also found itself playing ‘Global Policeman’ with the abolition of slavery, world over and engaging its Navy to stop the trade, especially along the west and east coasts of Africa. But it did not stop at just its Navy, it uses every means at its disposal, military and legal. On indentured labour/slavery, British policy would remain a little hazy as they practiced the system in Natal bringing indentured labour to work primarily on the sugar cane farms – both servitude and highly exploitative in nature Indian indentured labourers started arriving in Natal from 16 November 1860, albeit a less forceful version that the old Dutch inboekstelsel system, the ‘Coolie’ system (now a derogatory term) focussed on adult labourers free willing to enter into a contract for five years in ‘bonded’ labour with no rights and thereafter as ‘free-men’ they were able to buy or rent land, houses and open businesses – and even form political groups – albeit these concessions (clipped by harsh ‘immigration laws’) were highly limited in terms of both opportunities and human rights (all of which however was certainly not the case in the inboekstelsel system where there were literally no real concessions at all).
The Orange Free State Republic
The Orange Free State Republic was established by a combination of ‘trek Boers’ and ‘Voortrekkers’ having settled there (there is a slight difference between these Boers depending on when these Boers left the Cape, one set are natural migrants, the other set protested the British. But here’s the confusing part and the rather inconvenient truth when it comes to the general narrative, it was a British territory BEFORE it became a Boer Republic.
So, when these ‘Voortrekkers’ and ‘Trek Boers’ entered the Transorangia territory, re-named the British Orange River Sovereignty in 1848, they were subject to anti-slavery laws – these laws remained in place when it was later mutually agreed at the Orange River Convention in 1854 that Britain’s Sovereignty be administrated by Boers and they could declare a Republic of their own, but only as a proviso that the Orange Free State Republic established 23 February 1854, remain a British Suzerainty state (vassal state) under British oversight – so no slavery allowed in the Republic of Orange Free State from the get go. Also, the Orange Free State would never attain full independence since its inception to its end, it would at all times be a British Suzerainty, even up to and including the South African War (1899-1902) i.e. The Boer War.
The Orange Free State, chose to ally itself with its sister state, the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR), in their dispute with the British leading to the South African War (1899 – 1902) and joined with the ZAR to invade the surrounding British Colonies and Protectorates in Oct 1899. The result to their declaration of war against Britain is a counter-attack which would see the Orange Free State Republic annexed by the British in March 1900 when they took their capital Bloemfontein, a mere 6 months after the Orange Free State declared war against Britain and it was officially renamed and ratified as the ‘Orange River Colony’ by the British a the end of hostilities in 1902.
A conglomeration of Boer Republics
The British at the Sand River Convention in January 1852 would allow the establishment and amalgamation of Boer Republics north of the Vaal River as fully autonomous, only on the proviso that they were not to practice slavery (indentured slavery was a different matter). Unable to practice slavery proper, they enjoyed their autonomy and they would come up with legal and social compacts which defined class structures and franchise along racial and ‘national’ lines, as at 1852 most would become part of the ZAR, however due to the very isolated nature of these Boer groupings the ZAR did not really start to take shape until 1860. So let’s look at all these Republics and consider the number of Republics formed by trekking Boers (Voortrekkers and Trek Boers) and what happened to them;
The Republic of Zoutpansberg (1835-1864), incorporated into the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR) as a result of the 1st Boer War against the British (Transvaal War).
The Republic of Winburg (1836 -1844) and The Republic of Potchefstroom (1837-1844) amalgamated after 1844 to form the Winburg-Potchefstroom Republic till 1848. Eventually incorporated into the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR).
Natalia Republic (1839 -1843), established after the Voortrekker victory over the Zulu nation at the Battle of Blood River, named Natália after the Portuguese term for Christmas (the day they discovered Natal). The Republic came to an end in 1843 when British forces annexed it to form the Natal Colony, most of the local Voortrekkers then trekked northwest into the the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR) – which held massive swathes of Northern Natal.
The Republic of Klip River (1847-1848), established by Voortrekkers and is now modern-day Ladysmith, the British annexed it as part of the Natal Colony, naming the township ‘Windsor’ and then later re-naming it ‘Lady Smith’ after Sir Harry Smith’s Spanish wife.
Lydenberg Republic (1849 – 1860), established by Voortrekkers, it merged with a second Voortrekker Republic, the Utrecht Republic (1852-1858) and then both merged with the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR).
Klien Vrystaat Republic (1876 – 1891), established by Voortrekkers on land bought from the Swazi King Mbandzini around a township they established called Piet Retief, now controversially renamed eMkhondo. The Republic was incorporated into the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR).
The Republic of Stellaland (1882 – 1883) and the State of Goshen (1882 – 1883), both Republics established by Boer mercenaries awarded the land by the Twana Chief Moshoette for their assistance in his battles against the Mankurwane and Montshiwa Tswana factions. The two Republics merged to become the United States of Stellaland until 1885. In a land grab the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR) annexed it, in response to the Tswana chiefs requesting protection from Boer expansion and aggression, in 1885 the British annexed Bechuanaland in two parts, the Bechuanaland Protectorate (modern Botswana) and British Bechuanaland (later part of the Cape Colony), the United States of Stellaland was annexed as part of British Bechuanaland.
New Republic (1884 – 1888), also established by Boer mercenaries brought in by the Zulu King Dinuzulu to defeat his Zulu rivals, their compensation was land along the Mfolozi River. The Boers declared it a Republic and ‘Vryheid’ its capital. Long and short after a lot of conformation between the British and the Boers and the British and the Zulu, it was incorporated into Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR) and after the South African War (1899-1902) it was incorporated into the Natal Colony by the British.
Republic of Upingtonia/Lijdensrust (1885 – 1887). Declared on 20 October 1885 as a Boer Republic, it was originally named Upingtonia, but changed its name soon after. In 1887, it was merged into German South West Africa (Namibia).
The British did it too!
So, here’s an inconvenient truth – one your school text book would have gleaned over, its not just a Boer disposition to declaring mini Republics everywhere in South Africa, British settlers in South Africa did it too. When diamonds were discovered in South Africa in 1866 a flood of treasure hunters, especially from England, streamed to the diamond Fields around Kimberley.
Ownership of the diamond fields was contested by the Boer Republics of the Orange Free State and the ZAR, as well as various other groups, including the Cape Colony, the Griquas under the leadership of Andries Waterboer, and the Batlhaping, who were ruled by Chief Mankuroane. Before the issue could be arbitrated, the ZAR President Andries Pretorius decided to act unilaterally and declare the Diamond Fields as theirs in 1870. The Immigrant miners were so enraged, a former British sailor called Stafford Parker organised his fellow countrymen and drove all the ZAR officials out of the area and on the 30th July 1870, the Klipdrift Republic was declared and by December of the same year about 10,000 British settlers had made their home in the new republic.
Parker was elected as the President of the new republic, which was also called the Digger’s Republic and the Republic of Griqualand West. The Republic existed for an extremely short time, on 27 October, 1871 the British took possession of it after the matter of the diamond fields was arbitrated, and declared as belonging to the Griquas and it subsequently became a British protectorate (the Griquas fearing future Boer aggression, and unable to effectively administrate diamond claims and foreign miners – called in the British).
Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek (1852-1877, 1881-1902)
The Zuid-Afrikaanse Republiek – sometimes outlined as the Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek (South African Republic) or Transvaal Republic or ZAR has two lives, the ZAR (1852-1877) was initially established by Voortrekkers, whereupon its Parliament (Raad) voluntarily dissolved its status as a Republic and requested the British to convert it to a British Colony called the British Colony of the Transvaal (1877-1881) instead. Dispute, mainly over taxes, land concessions to African tribes made by the British and issues surrounding Boer sovereignty, eventually kicked off the ‘Transvaal War 1880-1881’ (or 1st Anglo Boer War) and the Republic was re-established as a Boer Republic after their victory over the British at the Battle of Majuba in 1881 – but only on PROVISO it too became a British Suzerainty state (vassal state) under British oversight – much the same status as the Orange Free State Republic.
The re-established ZAR (1881-1902) was again the main protagonist in the dispute with the British (over many reasons to be discussed another day) leading to the ‘South African War’ (1899-1902) hence the official name of the name of the war (not the “Boer War”). The ZAR’s invasion of British Colonies and Protectorates in Oct 1899 (not just the Cape and Natal Colonies, the ZAR and OFS Republican forces also invaded the Bechuanaland protectorate i.e. Botswana and Southern Rhodesia) and it would signal the official declaration of war, the British counter-attack would see the ZAR conventionally capitulate its capital 9 months later. The ZAR would cease to be a Republic and became a British colony again when it was re-proclaimed as the ‘British Colony of the Transvaal’ again on 1st September 1900 (after Pretoria fell to the British in the June of that year) and ratified it as a British colony at the end of hostilities in 1902. It remained The British Colony of the Transvaal (1902-1910) again until Union.
As a ‘fully independent’ Boer Republic, free of another Nation states’ oversight (Britain), the ZAR only really existed for a mere 15 years – but this did not deter the desire for ‘freedom’ from Britain by many of its white Boer population, and this was reinforced by the devastation to their society and economy caused by the South African War (1899-1902) or 2nd Anglo Boer War.
The idea of a ‘Union’
The ‘British’ i.e., the United Kingdom is essentially a union of four separate nation states with varying degrees of devolved authority. It is not a leap in logic to see how the idea of a union has resonance with them. As early as 1875 The Earl of Carnarvon, Henry Herbert – the British Colonial Secretary, approached the Orange Free State and the Transvaal Republics and tried to organise a federation of the British and Boer territories modelled on the 1867 federation of the French and English provinces of Canada.
The liberal Cape government also objected to the plan for ideological concerns; Its formal response, conveyed to London via Sir Henry Barkly had been that any federation with what were regarded as “illiberal” Boer republics would compromise the rights and franchise of the Cape’s Black citizens, and was therefore unacceptable.
Although this initial attempt of Federation by Henry Herbert failed, the concept remained. By 1902 the landscape of Southern Africa had changed with many more British territories bordering the old Boer ones, not just the Cape Colony and the Natal Colony, it included Rhodesia South (now Zimbabwe) and North (now Zambia) and the British Protectorates of Bechuanaland (now Botswana), Lesotho and Swaziland in addition. Some sort of peace and balance between these two antagonists was needed to allow for a stable governance of the region, the Boer Republics lay in tatters after the war, but the desire and fight to re-establish them remained.
The British were only able to secure a Peace treaty with the Boers at the end of the South African War (1899-1902) – on the CONDITION that Boer self-governance would be re-examined again in the near future. The British had also insisted that The Cape Franchise (a vote for Blacks based on a qualified franchise) be extended to include the old Boer Republics as a Peace Term to end the Boer War, bringing the issue of political emancipation for the region’s Black population sharply into focus.
General Jan Smuts attending the Peace negotiations with the British, was not only a skilful ‘Bitter-einder’ Boer General but also a skilful lawyer. Smuts was able to convince the British to put this issue of ‘black franchise’ on a back burner to be dealt with by a ‘future’ and ‘independent’ government in South Africa making its laws suitable to the region and not Britain insisting on applying its Westminster laws on the unwilling Boers. This would allow the old conservative Boer Republic’s laws on race division and exclusion to be upheld in their regions and the more liberal Cape Colony and British Protectorate laws on race inclusion to exist in their regions, at least for a little longer until the well-meaning British Colonial and Boer Republic ‘white’ politicians living in South Africa could resolve it.
The British would leave the amalgamation of their interests in Southern Africa with those of the Boer Republics interests to a future government in which the Boer Generals would have a significant say. So, long and short, something had to be done.
So, here’s some inconvenient truths, very often on Boer War forums, a grouping of Boer Romantics still hung up on Pakenham’s idea that the war was all about gold and diamonds, flat ignore the British historians who repeatedly point out it was about suffrage and human rights (both ‘miners’ in the ZAR and the black population groups inside or adjacent to the two Boer Republics). The Boer Romantics dismiss this as Britain paying “lip service” to African rights and not really that serious about it. However, look at this way – to end the Boer War, the first proper round of peace negotiations where held at Middleburg in February 1901, and the British demanded a “colour blind” qualified franchise, as existed in the Cape and other British territories be extended to the Boer Republics in addition as a peace term. The British also insisted on ‘representative’ governance of the Boer Republics after the war (mainly dealing with the quick inclusion for disenfranchised ‘foreign’ white miners in the ZAR in their political process and the establishment of their political ambitions).

So important to the Boers that their racial laws and franchise constructs remain in place, that they rejected these terms outright and walked away from the peace table. The uneasy truth is they were prepared to continue the ‘Guerrilla Phase’ i.e. Bittereinder campaign and endure the scorched earth farm burning policies and the displacement and death of their women and children in concentration camps for 13 more months of really savage war, rather than concede to a more representational system of government – and the British on the other hand were well prepared to continue such was their resolve.
The issue of a ‘black’ franchise would remain on the cards and even laid down again in May 1902 at the Treaty of Vereeniging (literally there were little real changes from the Middleburg Feb 1901 conference’s terms of surrender other than some British concessions on the Cape Rebels and an increase in war compensation funds to fix damaged farms), and here the issue of black enfranchisement was kicked into the long grass with the assurances and promises from ALL the Boer Generals (not just Botha and Smuts) that it would be dealt with in a future self-governance construct (the future ‘Union’). This is NOT just “lip service” as to human rights on behalf of the British, or for that matter the Boers – the issue was costing lives and of course this was not the only issue the Boers walked away from the negotiation table over in 1901, but it certainly is a major and on-going ideological dispute between Boer and Brit.
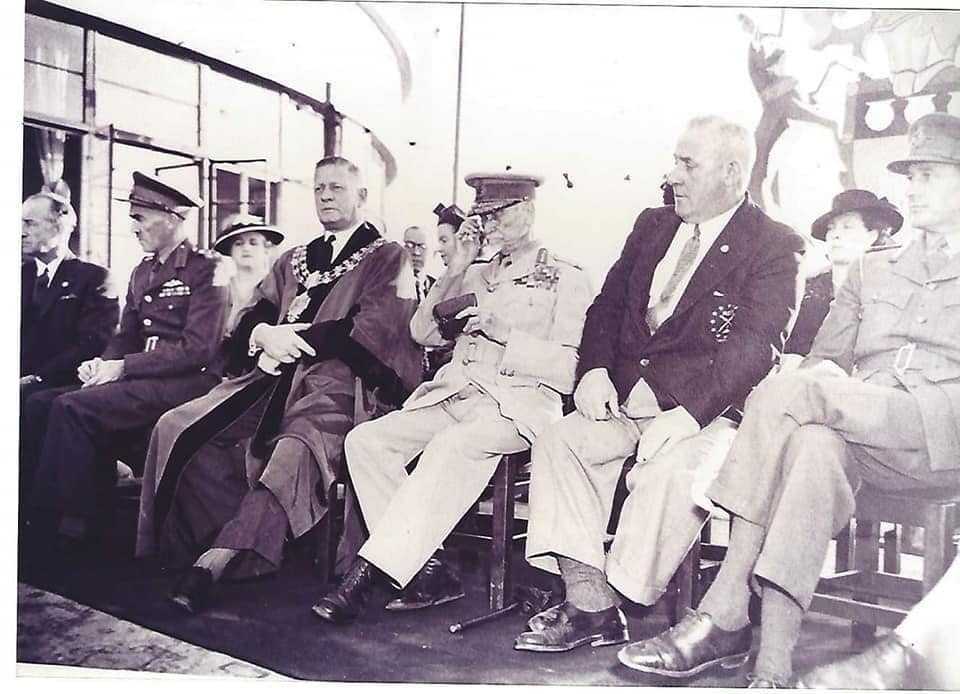
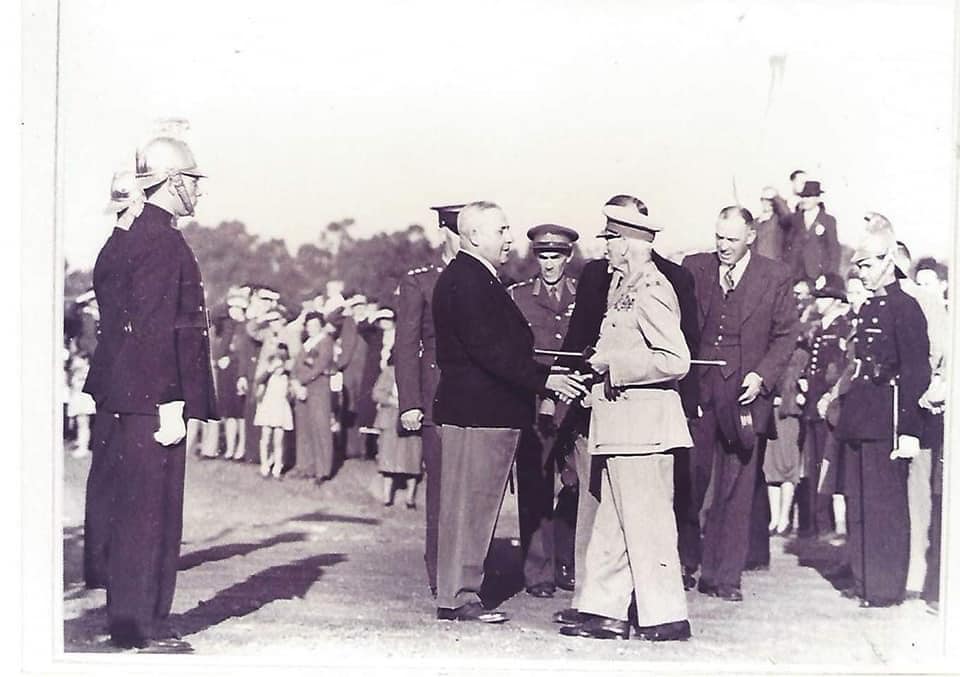
A well-meaning congress of ‘Closer Union’
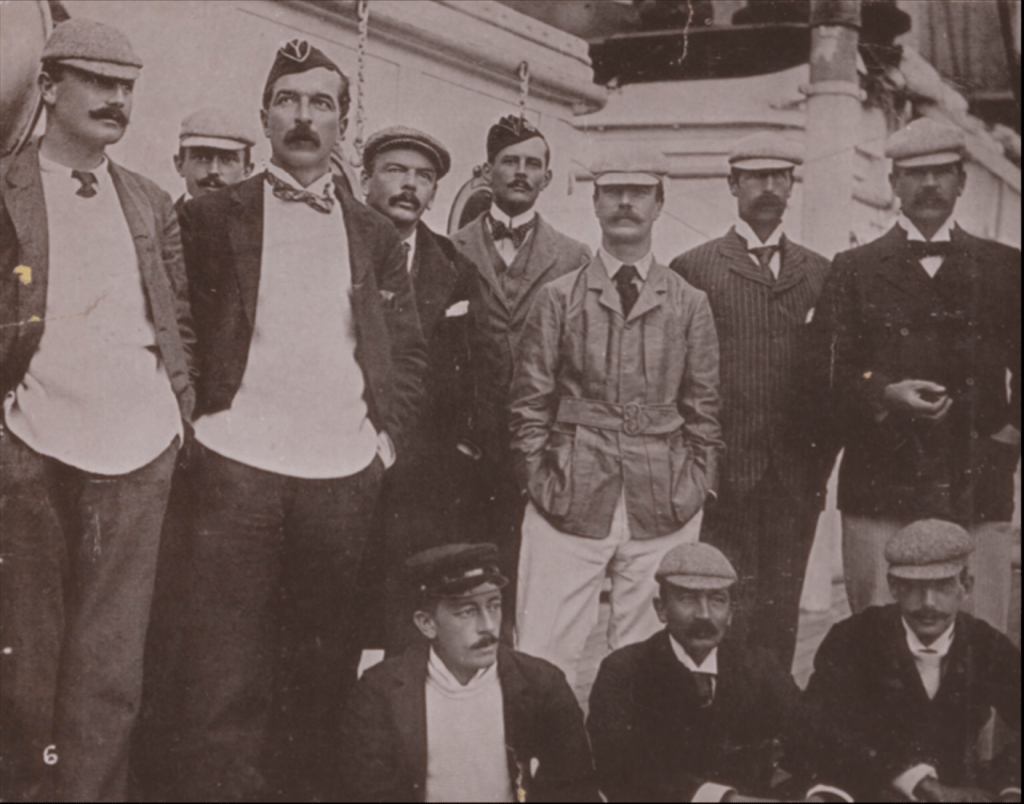
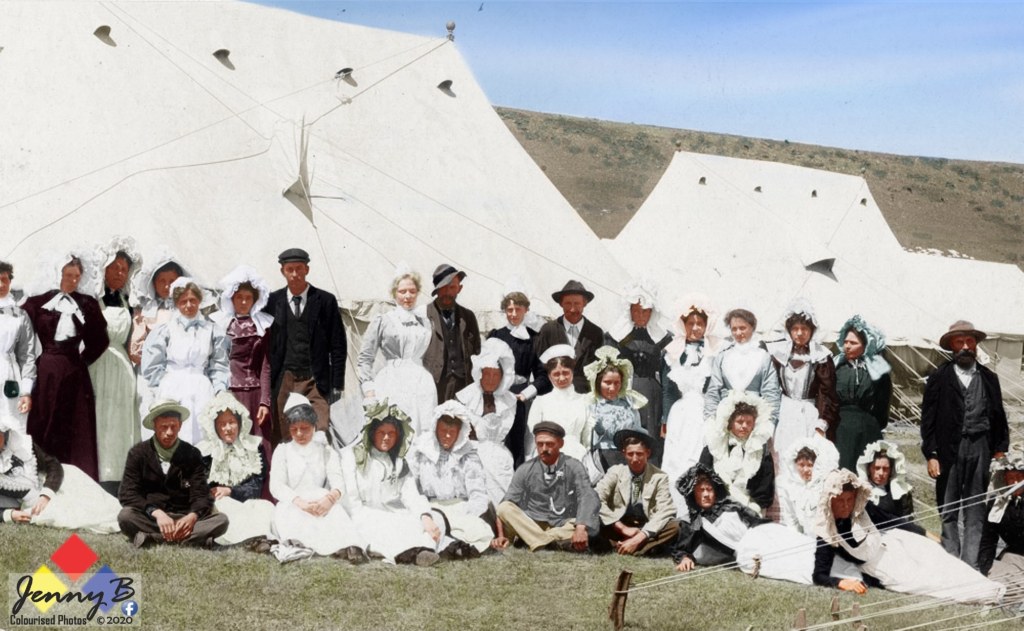
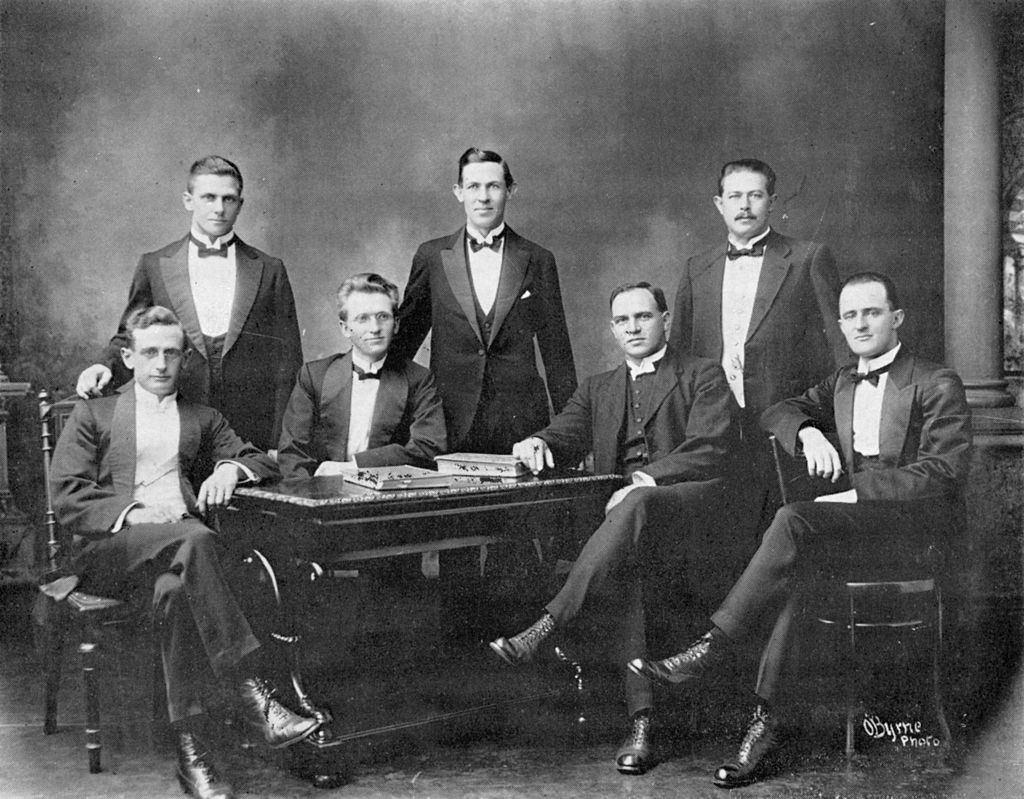
So, all the protagonists put aside their vast differences aside after the end of the South African (Boer) war in 1902 and got together to nut out a solution in 1908 and 1909, known as ‘The Closer Union Convention’ it was the CODESA of its day, a ‘whose who’ of modern Southern African history .., the old ‘Boer’ Generals – de la Rey, Hertzog, Smuts, Botha, de Wet and Burger even sucked it up long enough to sit opposite the likes of Starr Jameson and be nice. Notably, it also includes Southern Rhodesia (more on this later). Have a look at this photo of it, it’s a stella cast of the heads and ministers of every British colony and ex-Republic (now a British colony) in Southern Africa.

Front row (left to right): Hon. J.W. Saner, (Commissioner for Public Works); Hon. J.X. Merriman, (Prime Minister, Cape Colony): Hon. M.T. Steyn (Vice-President of Convention); Hon. A. Fischer, (Prime Minister, Orange River Colony), Lord J.H. de Villiers (President of the Convention), Right Hon. General Louis Botha, (Prime Minister, Transvaal); Right Hon. F.R. Moor, (Prime Minister, Natal), Sir W.H. Milton (Administrator of Southern Rhodesia), Sir J.P. Fitzpatrick.
Second row: Hon. E.H. Walton; Hon. Colonel E.M. Greene (Minister of Railways and Harbours); Mr H.C. van de Heerden; Dr J.H.M. Beck, Mr G.H. Maasdorp, Mr H.L. Lindsay; Hon. F.S. Malan (Secretary for Agriculture); General S.W. Burger; Hon. Dr T.W. Smartt; Hon. General C.R. de Wet (Minister of Agriculture); Right Hon Dr L.S. Jameson; Hon. H.C. Hall (Treasurer); Hon. General J.B.M. Hertzog (Attorney General); Mr C.F. Kilpin (Clerk of House of Assembly and Chief Secretary of Convention).Third row: General J. H. de la Rey; Mr W.R. Morcom; Hon A. Brown; Mr T. Hyslop; Mr J.W. Jagger; Hon. C.J. Smythe; Sir G.H. Farrar; Hon. General J.C. Smuts (Colonial Secretary); Mr A.M.N. de Villiers (Clerk to House of Assembly, ORC and Secretary of Convention).
Fourth row: Mr G.T. Plowman (Secretary to the Prime Minister of Natal and Secretary to Convention); Mr W.E. Bok (Private Secretary to Prime Minister of Transvaal); Mr G.F. Hofmeyr (Clerk of House of Assembly Transvaal and Secretary to Convention); Colonel W.E.M. Stanford; Hon. C.P.J Coghlan.Mahatma Gandhi would even speak at the Conversion and bring up the issues surrounding Indian indentured labour immigration, Indian ‘free passengers’ and all of their rights. The solution they all came up with, a ‘Union’ was needed, a grouping of federated states, much the same as had been proposed in 1875 by Henry Herbert along his ‘Canadian model’. It would publish ‘The Framework of Union’ explaining the ‘Union’s’ constitutional frameworks as following the likes of the United States of America and Canada. It would then go on to lay down the constitutional framework for the future South African Union.
However, key to this ‘balance’ of British and Boer interests and unity would be the eventual inclusion of Rhodesia in the South African Union, also key would be the eventual inclusion in the South African Union of the British Protectorates of Bechuanaland (Botswana), Lesotho and Swaziland.
What’s missing from this well-meaning congress? Clearly it was the Black African political representatives, this idea of Union was to be progressed without their input. Clearly, they needed a political voice as a homogenous group of ‘Africans’, and it’s a large reason why The African National Congress was formed just 4 years later in 1912, originally as the South African Native National Congress (SANNC) and made up of a ‘conservative’ African intellectual class – ‘Christian’ in its central ideology.
Also, from the outset, the degree of ‘devolved authority’ to the ‘federated states’ was an issue. The Union of South Africa would carry a highly ‘centralised’ government and the likes of Olive Schreiner who was vehemently opposed to a centralised system of government for the new Union and advocated a highly devolved confederation instead, and berated the negotiators as being “men selling their souls and the future.” She, was not wrong, and as we will see in the future, the ‘centralisation’ of government would undermine the future ideals of ‘greater union’ after 1910 and also find a happy matrimonial bed for the South African ‘Banana’ Republic to thrive after 1994.
The South African Union … and it’s not what you think!
This is an expansive subject, bear with me, I’ll make it as brisk as possible. Let’s look at the ‘Union’ argument for South Africa, and upfront this is going to shock many – The South African Union as we know it, is not the South African Union that Smuts and his cronies envisioned, not by a long shot.
The central mechanism to attain ‘Union’ from the Boer perspective starts is a little known political party called ‘Het Volk’ – a party essentially led by a Louis Botha and Jan Smuts in partnership, and a party that would eventually pull together all the old Boer war Generals (including Hertzog) and the leading British Colonial parties into a unified entity – ‘The South African Party’ (the SAP or ‘Sappe’). Its mantra was ‘Union’, its chief philosophy was ‘reconcilliation’ and its chief visionary – Smuts.
For all the ballyhoo of Nelson Mandela being the ‘father of South Africa’ that’s not true, the ‘father of South Africa’ was Jan Smuts – period, and Smuts did not envisage South Africa on its current borders – it was much much bigger. Even before The South African War (Boer War) 1899-1906, the Afrikaner Bond, established in 1881 had as its stated aim a unitary Afrikaner Republic from “the Cape to the Zambezi”, even Smuts had already started articulating his views a greater ZAR incorporating the British colonies from 1895, Kruger and his cabal had always been expansionists – bear in mind ‘Swaziland’ was not a British protectorate at the start of the Boer War, it was annexed by the Zuid-Afrikaanse Republic (ZAR) in an expansionist grab, along with more bits of Zululand in a bid to extend the borders to include a eastern sea port, plans and threats were even afoot for a Boer invasion of southern Rhodesia – the Adendorff trek. In fact ‘Botswana’ as we know it now was established to protect the Tswana from Kruger’s ever westward expansionism – now, not many people know that!
Cecil Rhodes thought the same way with his British South Africa Company, only his idea specified ‘British influence’ – hence the clash of under ‘whose influence’ and whose ‘laws’ all this expansionism and regional control would take place (British Unionist or Boer Republican) – its an ideological clash between Boer and Brit.
To conclude the Boer War, the Peace Treaty at Vereeniging settled the issue under whose influence all this imperialism, expansionism and unionism would take place – either Boer or Brit. The British demanding a settlement as long as South Africa remained part of the British family of nations, and with the goal of ‘self government’ for the entire region – to be shared by both ex-Boer Republic and ex-British Colony leadership.
By the conclusion of the Union Congress in 1909, the declaration of Union in 1910, and the conclusion of World War 1 in 1918, Smuts’ vision for a Greater South African Union bordered on a ‘United States of Africa’ on a federalism ideology. A proper Union, a system of inter-dependent states pivoted around Smuts’ central philosophy of ‘union is strength’ a philosophy which would all eventually evolve into his philosophy of ‘holism’.
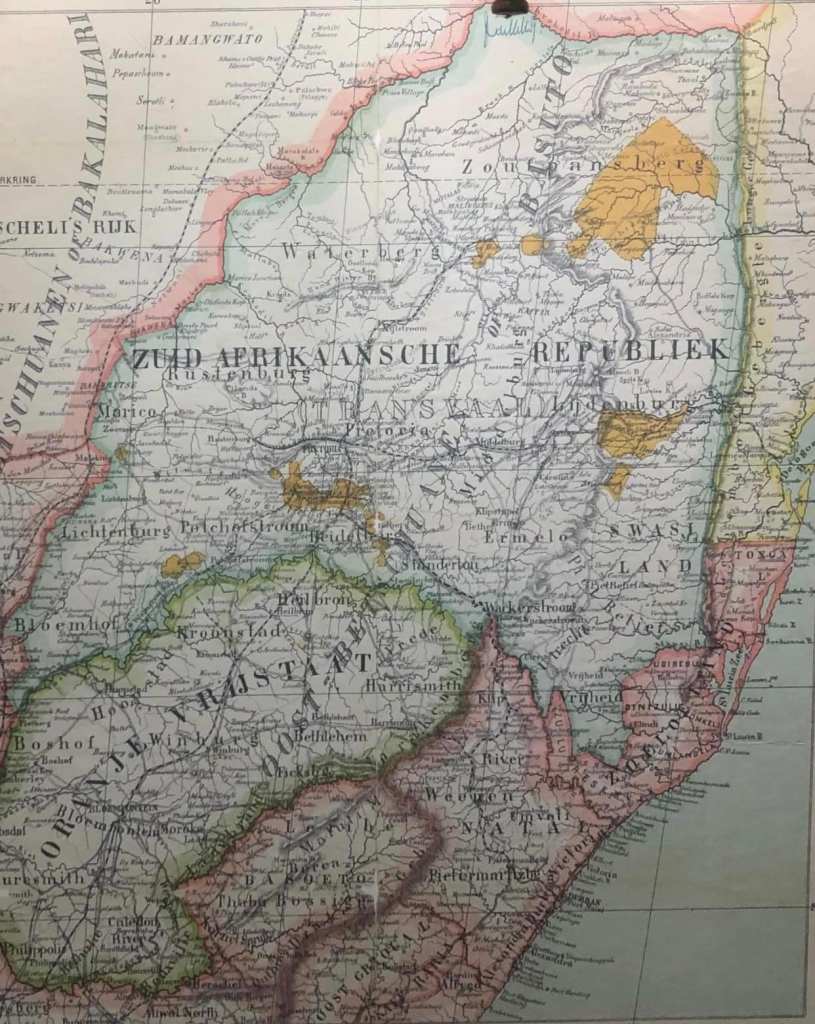
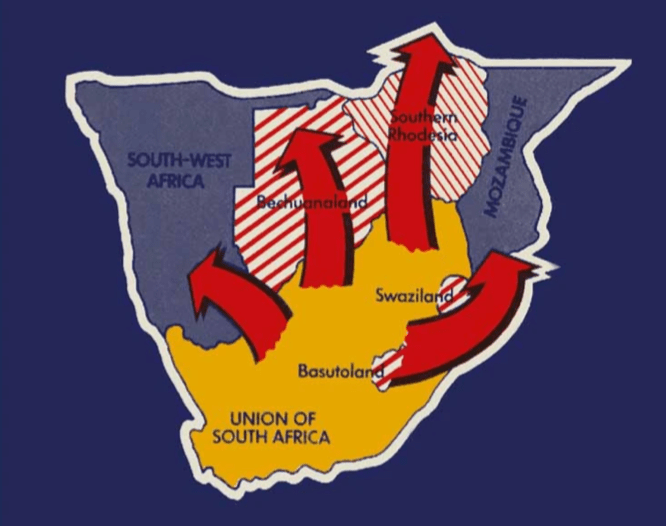
Smuts’ expansionist thinking took South Africa’s borders over the Zambezi River – literally all the way to the equator. Here’s Smuts’ map of it, and note his personal marks of A and B, the map is in three phases:

Image: Jan Smuts’ map marking the phases of Union
Phase 1, the initial South African ‘Union’, which would incorporate Lesotho and Swaziland.
Phase 2, this would be followed by the incorporation of Bechuanaland (Botswana), German South West Africa (Namibia), the southern half of Portuguese East Africa (Mozambique – Delagoa bay) and Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe).
Phase 3,’Greater South Africa’ does not stop at Phase 2, the next phase would see half of modern Angola, the rest of modern Mozambique (the north part of Portuguese East Africa), the whole of modern Zambia (Northern Rhodesia) and the whole of modern Malawi joining the South African ‘Union’.
So, what went wrong with a Federation?
So, we nearly had a ‘United States of Africa’ a Federation of individual states like Australia, the USA, United Kingdom and Canada – bet you didn’t learn that in your history books. Life may have seen substantially different – Apartheid would probably not have happened, Rhodesian UDI would probably not have happened, even the Angolan Border War would probably not have happened (Southern Angola and SWA would have been part of the Union). So, what was right with the thinking and what was wrong?
On the right side was Smuts’ ideals of globalism and holism – the inter-dependency of peoples, nations and cultures on one another (politically and economically) – this thinking would see Smuts steer in the ideals of the Commonwealth of Nations (instead of ‘Empire’), the United Nations (instead of the League of Nations), and the same philosophy has been implemented after Smuts’ death in 1950 – we’ve seen European Economic Union and closer to home ‘BRIX’ and the Southern African Development Community (SADC) zone.
On the down-side was this persistent problem of Afrikaner Nationalists demanding Republicanism in their likeness, and the on-going issues of segregation and ‘white’ Imperialism in the territories concerned. Even Smuts saw this ‘United States of Africa’ under some sort of white patronage with a qualification franchise to gradually bring Black indigenous tribes into the edicts of western democracy – a gradual transformation to full political emancipation within institutions of western governance – and who can blame Smuts here, even as liberal globalist and a man ‘ahead’ of his time, he was also a pragmatist and a man ‘of’ his time. Smuts understood and often said “a politician cannot move faster than his electorate” (or lose his ticket) – and in his case his electorate was mainly ‘white’ and intensively racially divided and very fearful of a ‘Black’ future.
However, the two big de-railers of this ‘United States of Africa’ were the white voters, suitably enfranchised in South Africa and Rhodesia – oddly, both diametrically apposed and in fear of one another.
At Union in 1910, it was hoped that British Protectorates of Bechuanaland (Botswana), Lesotho and Swaziland would be incorporated. The difficulty in Smuts’ dream was the word British ‘Protectorate’ – they were not British ‘Colonies’. They could not be legally forced into Federation; they were tribal Kingdoms (and still are) and had all requested British protection in response to Boer expansionism and to avoid being swallowed up by the Boer republics.
These Protectorates opted on a ‘wait and see’ strategy – wait to see what ‘Rhodesia’ would do, as this would ‘balance’ Afrikaner nationalism and its race laws which were still apparent in the old Transvaal and Orange Free State legal constructs, Botha and Smuts had still not been able to institute the black qualification franchise vote as required by the British at the end of Boer War in 1902.
Thomas Pakenham (a travel writer and Irish Republican) would make one very good conclusion in his first authoritative work considered history ‘The Boer War’ – and its one which we can agree on, he said the Boer nation would never concede a vote franchise to the Blacks, regardless of promises given and would conclude that the nation which truly came off the worse in Boer War 2 was not the Afrikaner one – despite the white concentration camps and scorched earth policies, but it was the Tribal Blacks and their nationhood who would be the greatest losers. Try as they might Botha and Smuts would never be able to shift this needle. If anyone is wondering why South Africa has great big holes in the middle of it comprising the Kingdoms of Lesotho and Swaziland – this is why. Botha and Smuts however went ahead with Union in the hope that this burning question of black franchise qualification would be settled by Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe).
With Southern Rhodesia on board, as was planned at the ‘The Closer Union Convention’ a year before in 1909, and even with the South African Act passed in 1909 which outlined ‘Union’ as it made way for the inclusion of Rhodesia as the 5th province in the Union. It would now be up to Rhodesia who would provide the balance between the main British territories of Rhodesia, Natal and Cape Colony – with their more liberated approaches to enfranchisement than those of the two old Boer Republics – and in the end the ‘majority’ of progressively minded whites in the region would win out and the small but burgeoning desire for ‘white’ Afrikaner Republics would be kept at bay by sheer democracy and a willingness for greater Union.
So, up to the Rhodesians to decide the future South African Union and political balance then. Winston Churchill once said, “The best argument against democracy is a five-minute conversation with the average voter” (incidentally Churchill was also then the Colonial Secretary to Southern Africa) and in the case of Union this became a truism as the Rhodesians took the matter to a referendum, they called a vote on the matter on the 27th October 1922. Option 1: ‘Responsible Government’ (own independence) or Option 2: ‘Union with South Africa’.
In Rhodesia, the prevailing government opinion was that Union with South Africa was inevitable, it was supported by the United Kingdom’s government, the South African government, and the British South Africa Company – all of whom favoured the Union option. But (like BREXIT recently), the government was out of touch. The Rhodesian enfranchised voters (mainly white, some black) were afraid of ‘Boer’ policy interfering in Rhodesian politics and fearing the extreme segregationist and race law issues latent in South Africa’s old Boer Republic provinces opted out of Union voting 59% in favour of ‘Responsible Government’ instead.
Thus ‘nearly’ ended any dreams Smuts had of a ‘Greater South Africa’ or ‘United States of Africa’. It was only 1922, and there was still time and the whole of German South West Africa to consider, which after it was annexed by the Union of South Africa during World War 1 was a South African ‘mandate’ with League of Nations oversight. Jan Smuts have even proposed it be re-named after his friend, fellow Boer General and now the Union’s first Prime Minister – Louis Botha as “Bothaland” (bet you did not see that in your school books either). Bothaland did not go ahead, but Smuts, determined that Union through ‘annexation’ go ahead and ignoring the League of Nations mandates he even tried (again) to name South West Africa as a 5th Province of the Union of South Africa as late as the 17th October 1946. The new United Nation’s defeating Smuts claims in 1946, reducing the Union’s powers over the territory and placing it under ‘Trusteeship’ instead (primarily concerned over black rights) – that was really the end of Smuts’ expansionist Greater South African Union as South Africa never really had ‘full’ legal authority over South West Africa in the past and now going into future, as hard Smuts tried, it never would have full authority and its mandate over the territory was later set by the United Nations to expire in 1966.
Many ex-Rhodesians today lament their decision, as without the power of a large Southern African Federation behind them, they would be left alone to deal with mounting political pressure, especially over the issues of franchise and political emancipation. It laid the bed-rock conflict and for ‘right wing’ Rhodesians trying to hold onto segregation and the qualified franchise system within a white parliamentary construct as long as possible to come to power and declare a “Unilateral Declaration of Independence” in 1965, led by a very conservative Ian Smith and form … you guessed it, a Republic! The Republic of Rhodesia 1970-79.
So, let’s look again to the other problematic part of the Union’s mandate – South West Africa (Namibia) for which act of full Union was (and remained) elusive, the voting population by way of white settlers was small, an all-white affair made up of conservative German settlers who were almost equalled in numbers by Afrikaner settlers venturing into the territory. They would eventually deliver the final blow and bring about the ultimate collapse of the ‘Union of South Africa’ and the forwarding of a ‘expansionist’ white Afrikaner Republic instead.
What! South West Africa (SWA) ended the South African Union – no way! Well, it did, and its also the reason the Nats hung onto it as tightly and as long as they did, even occupying it with sheer military and police force when the South African mandate over the territory expired in 1966 – kicking off the Border War 1966-1989, so here’s why SWA was so important to the National Party and how they did it:
The Nats and their South African Republic.
The return of the idea of a Republic starts with the formation of the National Party in 1914 by Afrikaner Nationalists soon after the establishment of the Union of South Africa. Its founding was rooted in disagreements of ‘Union’ among South African Party politicians (remember ‘Het Volk’ and the formation of the SAP), particularly Prime Minister Louis Botha who sought a ‘unitary’ Unionist state with singular purpose called ‘one-stream’ and his first Minister of Justice, General J.B.M. Hertzog who sought a ‘two-stream’ state which separated English and Afrikaners.
Incorporated into the ‘Two-Stream’ ideology was the fierce adherence to ‘Krugerism’ – the racial separation and ideological purpose of the old Zuid-Afrikaanse Republic (ZAR) separating not just Afrikaner and English but also all the ‘Bantu’ in addition. With a oligarchy philosophy underpinning it, and the sense of ‘Boer’ Nationalism ahead of all other races in servitude to the Boer cause, the religious reincorporation of the ‘Chosen Race’ – white supremacy in effect. The ‘Politics of Pain’ also factored into the Nationalist ideology – i.e. the need to preserve Afrikaner identity by what was defined as a century long British tyranny, which ultimately manifested itself in the destruction of Boer farms and families during the 2nd Boer War. In essence it generated a victim mentality, and this preservation of Boer Nationalism and identity was paramount to the survival of the ‘Boer’ race – and if that required the subjugation by force of the ‘British’ and all other races and cultures threatening its ‘survival’ for that matter, then so be it.
The formation of the National Party was directly at odds with the aims and objectives of the Closer Union Convention of 1909 – the convention designed to end the Boer and British antagonism for once and for all.
Apartheid as an ideology had not really fully and clearly taken shape at this stage, the Nationalists were pretty loose in defining exactly how they intended to implement ‘Krugerism’, they sat in the pound seats running South Africa in coalition with the Labour Party (the ‘Communists’ in effect) after the Miners’ Strike in 1922 and in ‘Fusion’ with Smuts’ United Party in 1934 generally supporting British Dominion and ‘Union’ – this caused a breakaway called the ‘Purified National Party’ on the 5th July 1935 which stood to the far right politically, under the leadership of Dr D.F. Malan – and it stood in abject rejection of Union and demanding the return to Afrikaner Republicanism along with clearer ideology on racial segregation called Apartheid – this was all ultimately resolved by two events really – the Great Trek Centenary Trek in 1938 and the Second World War (1939-1945).
Henning Klopper, the Chairman of a young and up and coming ‘Broederbond’ initiated the 1938 Great Trek Centenary Trek to artificially bind and brand ‘all’ Afrikaners as decedents of the pioneers (Voortrekkers), symbolic of a ‘white’ Afrikaner hegemony paving the path of future unitary South Africa under white Afrikaner patronage. Long and short, although very fantastical and completely historically incorrect – it worked.
Afrikaner Christian Nationalism as an ideology outlined by the Broederbond as their official ideology, using the ‘Voortrekkers’ as a binding source of National pride and identity, would ultimately come to define ‘Afrikanerdom’. Even today, if you search ‘Afrikanerdom’ on-line you get a ‘whites-only’ Nationalistic hegemony of what qualifies an Afrikaner.
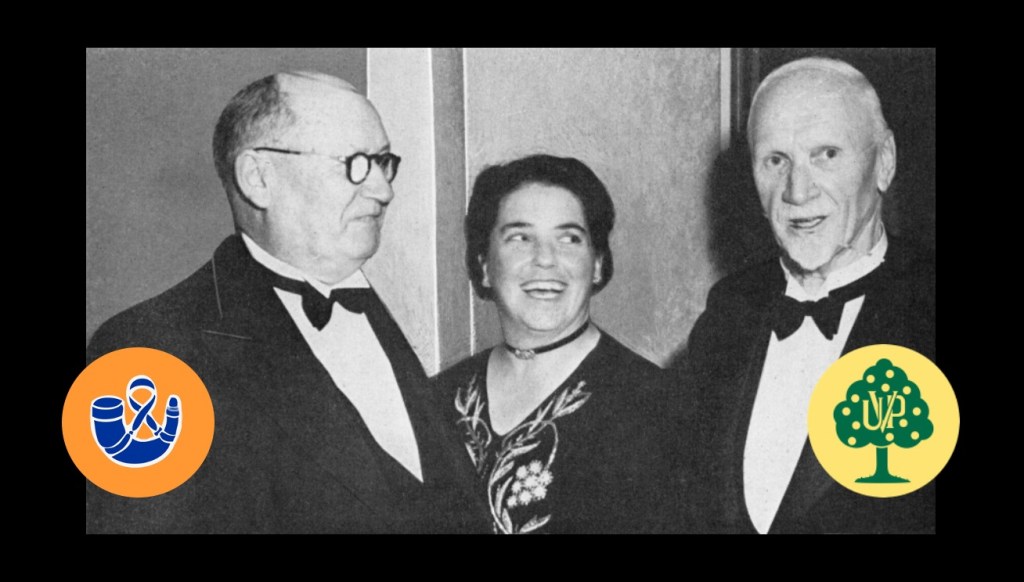

Smuts (right) and D.F. Malan (left)
Dr D.F. Malan would define the National Party’s ideology of Afrikanerdom when he said in November 1939. “An Afrikaner is one who, whether speaking the same language or attending the same church as myself or not, cherished the same Nationalist ideas. That is why I willingly fight against General Smuts. I do not consider him an Afrikaner.” An Afrikaner, in other words, was one who was prepared to accept the hegemony of the National Party and not those Afrikaners inclined to Unionism, Libertarianism or Liberal Democracy in the United Party and certainly not those like Bram Fischer in the Communist Party. This idea of ‘Afrikanerdom’ also did not extend to Black and Coloured Afrikaners or even Jewish Afrikaners who identified themselves as such.
Christian Nationalism would also be adopted by the Ossewabrandwag – the Ox-Wagon Fire Watch or OB which originated because of 1938 Centenary Great Trek (named because the Centenary trek spread Christian Nationalism and Afrikaner Nationalism like ‘wildfire’), an organisation which drew over 250,000 plus Afrikaner members under the auspices of a ‘cultural society’ on a ‘anti-British’ ticket – and was ultimately infiltrated and coupled to the ideologies of National Socialism (Nazism) through its leadership and their love affair with Nazi Germany and Adolf Hitler.
The Ossewabrandwag along with other Pro-Nazi Germany organisations like the ‘South African Gentile National Socialist Movement’ or Greyshirts, the ‘National Socialist Rebels’, the ‘Blackshirts’ and Oswald Pirows’ ‘New Order’ ensured that the ideology of National Socialism and Christian Nationalism was fused when all these movements were folded into the ‘Purified National Party’ – now re-named just the ‘Herenigde’ (Re-united) National Party’ after Hertzog resigned over Smuts’ decision to go to war against Nazi Germany. Only this time the Re-United National Party and its Afrikaner nationalists are now powered by a white supremacist nationalist cocktail of Nazism, Christian Nationalism and Apartheid – focussed solely on doing away with Union and implementing a ‘White’ Afrikaner Republic instead, they would undo all the work done by progressive Afrikaners like Smuts and Botha and well-meaning English South Africans of British origin – D.F. Malan and his cabal went on the political path with this sole objective in mind and time and again declared their aim for a Afrikaner Republic – where ‘English’ citizenship would take a de-facto secondary status along with all other ‘Non-Afrikaners’ like Jews, Indians, Coloureds and Blacks.
We all know about Jan Smuts’ shock defeat in 1948, where an Afrikaner Party coalition comprising The Re-United National Party and the Afrikaner Party squeezed out the United Party on the back of substantive gerrymandering and a fear campaign driving discontent over future black enfranchisement, after winning the two Afrikaner Parties merged to re-establish their original name – the National Party – however, a significant problem existed for the National Party’s dreams and promises of a Republic – their win was not a popular (majority) vote win at all – the majority of whites (English and great many Afrikaners) and the Cape Coloureds did not vote for Apartheid (in 1948 more or less as numbers go – 550,000 voted against Apartheid as opposed to 450,000 who voted in favour), and therefore the National Party still did not have the majority necessary in Parliament to change the South African constitution from a Union to a Republic (another inconvenient truth to the current ANC narratives – the majority of whites, regardless of privilege – did not vote for ‘Apartheid’).
So, what did the National Party do to get their Republican dream, well they cheated really, to gain their majority of 2/3 for a constitutional change they needed to pack the senate with more National Party friendly seats, and they needed to get rid of the Coloured Franchise (remember – in the Western Cape ‘Coloureds’ and Whites were on the same voters roll since the abolishment of slavery and ‘apprenticeships’ from 1853).
The National Party proposed legislation called ‘the Separate Representation Act’ in 1951 to remove ‘Coloureds’ from the Common Voters Roll. Amongst other measures to negate and by-pass the judiciary, they turned to ‘South West Africa’ to push their majority.
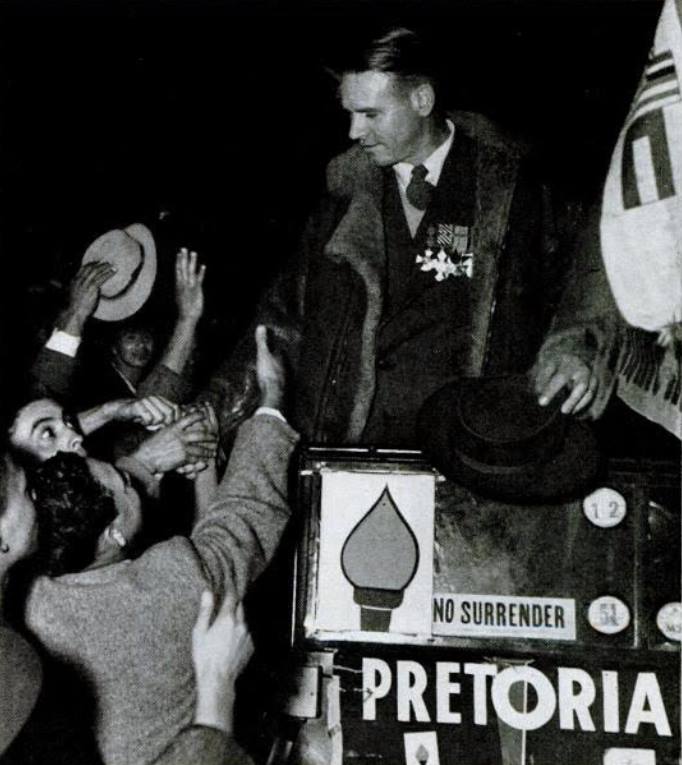
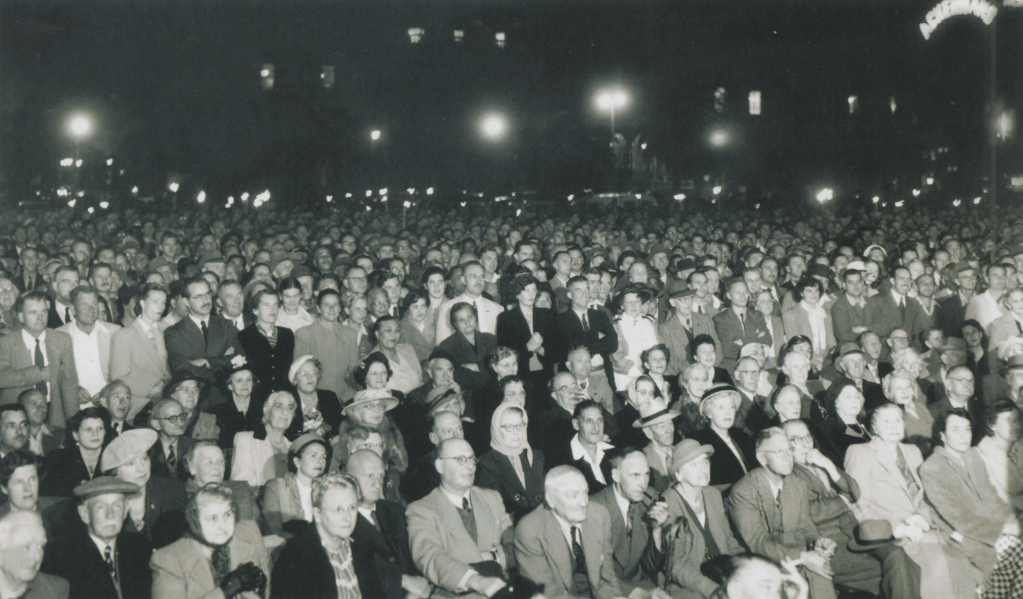



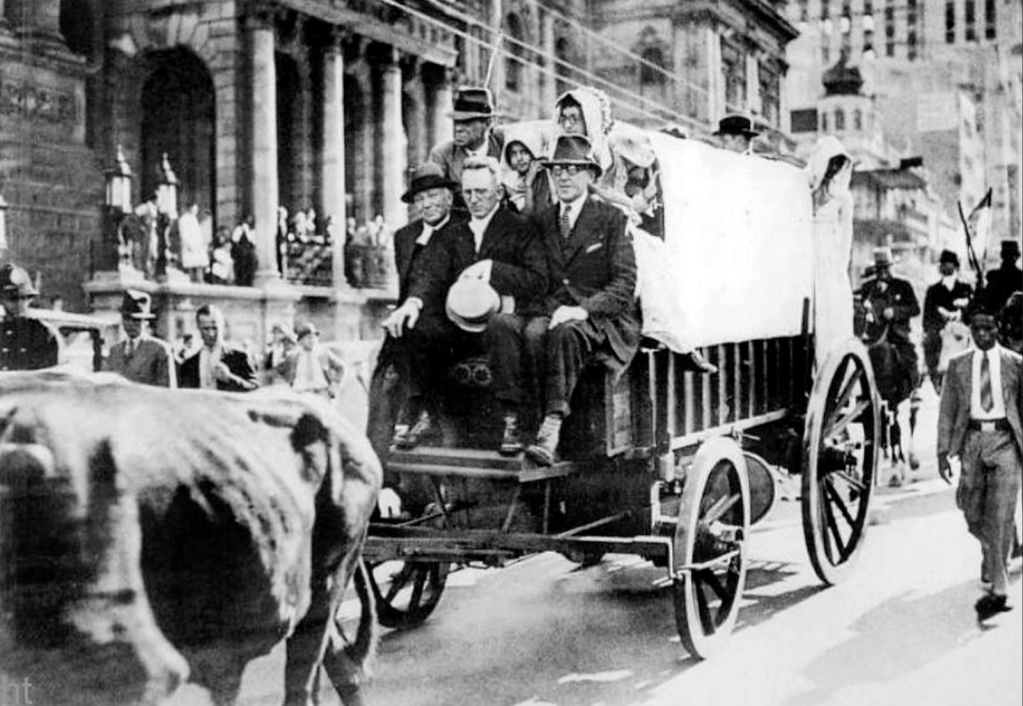
Images : The Torch Commando, 250,000 white people alone in open protest countrywide against the removal of Coloureds from the common voters roll and the advent of a ‘Facist Republic’ (see rally placard) – a quarter of the white vote bloc on the streets protesting and demanding the resignation of the National Party government.
As discussed earlier, convenient for the National Party was Smuts’ old Unionist expansion plan, where Smuts had looked to Rhodesia to ‘balance’ Republican politics in South Africa, now with Rhodesia out of the equation, the nationalists looked to South West Africa to reinforce their Republican politics (and if you are an old SADF vet who still thinks you were only in SWA to fight communists – this next bit is going to sting a little manne).
One of the first acts passed when the National Party came to power in 1948, was the South West Africa Affairs Act of 1949 Amendment, which went against the wishes of South West Africa’s Trusteeship in the United Nations – it ‘illegally’ gave representation in the South African Parliament to whites only in South West Africa, it gave them 6 seats in the South African House of Assembly and 4 seats in the Senate and it also illegally gave all whites in South West Africa a vote in South African affairs and elections.
This was to the advantage of the National Party who enjoyed strong support by the ethnic Germans as the National Party had through many of its organs expressed support for Imperial Germany and subsequently Nazi Germany during the two war world wars. Such was the support that from 1950 to 1977 all of South West Africa’s parliamentary seats in South Africa’s Parliament were held by the National Party.
On the Cape Coloured Franchise, The Separate Representation Act as put forward by the National Party in 1951 went ahead after the National Party overcame the powers of the judiciary through packing it to by-pass the constitution. The ultimate removal of the Cape Coloureds (some 50,000 voters) from the Common Voters roll in 1956 would pave the way for future and more sinister racially based Apartheid legislation, the complete marginalisation of ‘black’ political representation and it would open the way to the National Party’s dream of a Referendum to take South Africa out of its British Dominion and ‘Union’ status completely to become a White Afrikaner Republic.
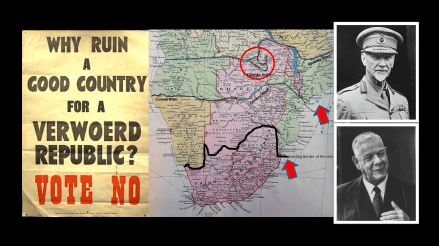
By 1960 the National Party was ready, Dr H.F. Verwoerd was now at the helm and a referendum on the matter of Union vs. Republic was held. Single question “In Favour of a Union or Republic” – yes or no. The heavy media campaign to propose the Republic was a “Unite and Keep South Africa White” proposition and the promise of white’s only enclave in South Africa (and SWA). The entire campaign and proposal rejected outright by the majority of South Africans. It went ahead on 5th Oct 1960 and the National Party won it, but by a sliver – 1%, only 70,000 votes – and here’s how the maths worked to do it.

Image: National Party Campaigner 1960
The illegal ‘white only’ sympathetic South West African (Namibian) voters gave Verwoerd 20,000 Pro-Republic votes and by unconstitutionally removing the Cape Coloureds from the Common Voters Roll he was able to minus 50,000 Anti-Republic votes. Then by ‘banning’ or ‘gagging’ almost all strong opposing ‘white’ voices in the Liberal Party, Congress of Democrats, United Party and Labour Party using the Anti-Communist Act and the ‘Treason Trial’ (which lasted from 1956 to 1961) – basically, silencing many white Unionist opposition almost completely. The Net result was the sliver of 1% – the 70,000 votes he needed for a ‘Republic’.
The result was a White’s Only Apartheid Republic, declared on the 31st May 1961 in which a foreign country’s white voters played a significant role in establishing the Republic, a Republic rejected by the British Commonwealth of Nations (from which South Africa almost immediately resigned – also read ‘kicked out’) and the near majority of voters in South Africa itself (whites), the Coloured community now disenfranchised and the Black Community when the ANC and Nelson Mandela personally formally rejected the referendum, his letter on the matter of Unions and Republics is most insightful when he said, rather prophetically:
“The adoption of this part of the resolution did not mean that (the ANC) conference preferred a monarchy to a republican form of government. Such considerations were unimportant and irrelevant. The point at issue, and which was emphasised over and over again by (ANC) delegates, was that a minority Government had decided to proclaim a White Republic under which the living conditions of the African people would continue to deteriorate.”



Images: 1960 Union vs Republic campaign.
On track to a Banana Republic
We all know the history of Apartheid, 1960 was the turning point, the massacre at Sharpeville took place on the 21 March 1960 and a white Liberal Party activist attempted to assassinate Verwoerd on the 9th April 1960 at the Rand Show by shooting him in the head. The immediate jackbooted swoop down on the progressive whites (English and Afrikaans) in the United Party, the Liberal Party, the Labour Party and all ‘Black’, ‘Coloured’ and ‘Indian’ political movements and parties by the South African police in 1960/61 was unprecedented, as they literally imprisoned, banned, gagged and deported many of the country’s leadership deemed ‘unpatriotic’ to the Afrikaner Nationalist cause. That action was to change the course of South Africa as it was to change the course of the African National Congress.
So what does the Apartheid Republic of H.F. Verwoerd possibly have to do with the mess we are in now, the ANC are responsible for the mess were in – not the Nats right? It’s an ANC Republic now. Well, wrong – the Afrikaner Nationalists and their desire for a Republic are as much responsible for African Nationalists and their desire for a Republic and the main reason … the “Politics of Pain”. Let me explain.
Remember the ‘Closer Union Convention’ of 1909 to remedy the antagonisms which under-pinned the South African War (1899-1902). The National Party came about in 1914 as they simply could not “bury the hatchet” and focus on Unionism – as a small fringe party at that stage (and they have always been ‘fringe’ in the greater sense of the population of South Africa), they were still determined in their focus of reinstating ‘Krugerism’ and the ultimate dream of a White Afrikaner Republic spanning from Cape Point to the Zambezi, sans British interference. The British had caused them substantial harm, starting with the indignation kicking off the Great Trek and ending with Boer War 2 as the British used scorched earth and concentration camp policies to ultimately win the Guerrilla Phase of the war – which had a massive impact on ‘Boer’ society and psyche.
Added to this in 1914 was the decision to go to war against German Imperial Axis forces in World War 1, by an independent Union of South Africa. By a vast majority vote in the South African Union Parliament comprising a majority Boer (SAP) government – a staggering 92 MP’s voted in favour of invading South West Africa and siding with Great Britain and only 4, yup – only 4 MP’s voted against (an inconvenient truth that’s often conveniently ignored by contemporary Boer Romantics today who repeatedly state the ‘majority’ were against “Smuts’ war”), this kicked off the Maritz Revolt in the same year 1914 – which again sought in its stated objectives to create a Afrikaner Republic, from the Cape to the Zambezi – and with the aid of the Imperial Germany via South West Africa they hoped see the British out (of South Africa and all its surrounding British protectorates) – aid which was never really forthcoming and a revolt doomed from the get go because of lack of any significant support and resolve, from either the Afrikaans or English communities.
At the same time, and forming in parallel to the National Party in 1914 is the South African Native National Congress (the original ANC), formed in 1914 also in response to Closer Union Convention’ of 1909 and the announcement of The South African Union in 1910, only this time they are on a mission of ‘inclusion’ – as they had been ‘excluded’ from the convention and their political aspirations and desires had not been properly accounted – sending their delegation to the United Kingdom in 1914 and again in 1919. Small beginnings, like their Afrikaner Nationalist counterparts they are also just burgeoning.
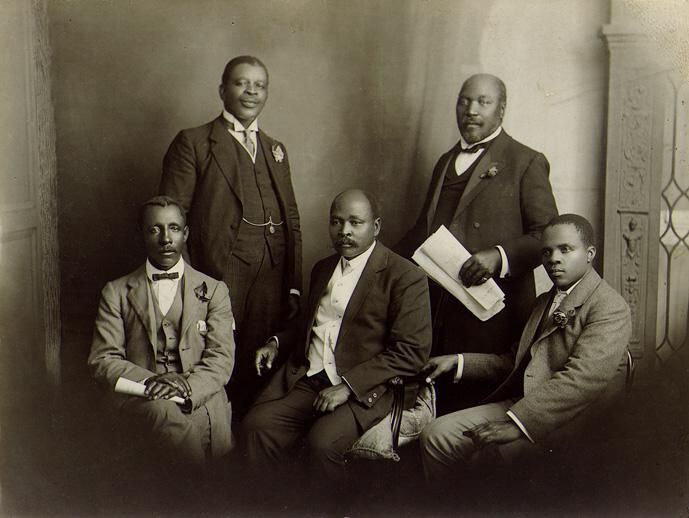

The ANC sought inclusion, representation and political emancipation throughout South Africa’s tenure as a ‘Union’ and calling on the United Kingdom to assist in this quest became their mission. At this stage the ANC is no means ‘radicalised’ – its central tenants are for the recognition of an African national identity. In fact, like the Afrikaner Nationalists, they were ‘Conservatives’ on the political spectrum – focused on protecting a moral and social order they correctly perceived to be under attack. They are also nationalists in the pure sense of it, aspiring to a unified National identity for all Black South Africans (regardless of tribe).
At this stage the ANC is also relatively happy with the idea of Union’s independence with British dominion oversight and protection as it is far more disposed to working with them to gain political emancipation than any Afrikaner Republic would. The ‘Politics of Pain’ although beginning to germinate had not yet fully entered their ideology and rhetoric as a full blown foundation stone, the advent of Apartheid in 1948 would see to that.
The Politics of Pain
This ‘Republicanism’ and ‘anti-British’ desire the Afrikaner Nationalists had was underpinned by the belief that the British had done the Boer nation an injustice, not just in 1899, this started with the abolition of their slaves in 1834 when small groups decided to leave the Cape Colony and start forming their own Boer Republics along racist lines, with their basis solidly rooted in Afrikaner “Nationalism”. This ‘injustice’ to their ‘freedoms’ begins the ‘politics of pain’ central to the concept of Nationalism – an injustice caused by the tyranny of another ‘nation’ on it, such that the survival of the repressed nation depends on it usurping its power over anything that would threaten it again and controlling its own destiny.
This led directly to the desire, and the eventual realisation of the Apartheid Republic. But in realising this Apartheid state in 1961, the ANC and all other opposition to it (including white) would need to be banned, murdered, imprisoned, gagged or exiled.
By 1960/1961 the ANC, a previous ‘conservative’ congress, was also forced into armed resistance and into coalition with the Pan African Congress (far left radicalised African Nationalists) and a tripartite alliance with ‘Labour’ – The Congress of South African Trade Unions (COSATU) and the Communist Party of South Africa (CPSA). With that came the journey of ANC from a ‘Conservative and Christian’ African Nationalist platform to ‘Sankarism’ and ‘African Socialism’ a heady concoction that at times even borders on National Socialism (similar to the old edicts of Afrikaner Christian Nationalism). This African Nationalist love affair with out-dated Communist and Socialist ideologies is something the ANC carries proudly on its sleeve and even through the world has moved on they continue to try and resurrect this socio-economic system – that it has been historically proven unworkable time and time gain and even seen by many ex-Communist countries as a crime against humanity is simply ignored. Yet on we go.
The politics of pain again, and it rears itself throughout the ‘Struggle’ years – injustice, pain and trauma caused to the Black population by the Apartheid state – and by the ‘white settlers’ not part of nation’s soil – foreigners, seeking to exploit their minerals and labour. To overcome this was the need to for a unified black consciousness who when it comes to power will seek to usurp its power over anything that would threaten the ‘Mzanzi’ Nation – a term now firmly entrenched in the South African national identity and lexicon. The penalty for ‘Apartheid’ – land and capital appropriation without compensation from the ‘white’ owners of it (in much the same way Nazi Germans appropriated through the same legislation – land and capital belonging to Jews).
Nationalism in a nutshell
Let’s examine ‘Nationalism’ for a minute – and this is Nationalism in the context of Hegemonic Nationalism, as said – to be this sort of Nationalist you need an extreme sense of ‘identity’ formed by a ‘trauma’ and a political and economic ‘enemy’. In the case of the Weimar Republic or German Reich (realm) 1871-1945 … before World War 2, the Nationalist Socialists (Nazi party) believing in a ‘Aryan’ (white) supremacy as to be a ‘proper German’ or sense of national identity, forms on the back of great injustice dealt to it by the ‘Allies’ (mainly France) during World War 1 – the war, its death and destruction and the indignation of the Treaty of Versailles leaves an enduring scar on the psyche on the German nation. So that’s the ‘Political’ enemy sorted, now for the economic -‘Jewish Monopoly Capital’ – the Jews profiteering from the misery of World War 1 and exploiting ordinary white Germans. The result – a German Reich run on extreme Nationalist lines with a very high incidence of state involvement and an Aryan nation’s survival guaranteed by drawing compensation from the state and its captured Jewish Capital, a race of peoples they were very happy to wipe off the face of the planet for their own ‘Aryan’ survival.
Afrikaner Nationalism – similar belief to National Socialism in Christian Nationalism i.e., a belief in an all-White Afrikaner hegemony to be a ‘proper Afrikaner’. Dealt a great injustice by the ‘British’ during Boer War 2 – the war, its death and destruction and indignation of the peace treaty leaves an enduring scar on the psyche on the Afrikaner nation. So that’s the ‘Political’ enemy sorted, now for the economic -‘British (and Jewish) Monopoly Capital’ the British profiteering from the misery of war stealing the Boer’s rightful claim to gold and diamonds and exploiting ordinary white Afrikaners. The result – a Afrikaner Republic run on extreme Nationalist lines with a very high incidence of state involvement to ensure the survival of the Afrikaner nation whilst drawing compensation from the state – and they went about it with all manner of cronyism setting up mineral and farm produce price fixing boards and creating monopolies and duopolies and state owned companies – even legislating ‘job reservation barriers’ and ‘colour bars’ ostensibly for White Afrikaner economic advancement only (the ‘poor white’ problem argued as a result of, you guessed it – the British and their Boer War 2 scorched earth policy).
African Nationalism, and here we look at African Nationalism as practiced under the principles of Sankarism and Pan-Africanism, which is central to the philosophy put forward by the African National Congress, its ‘RET’ Radical Economic Transformation faction and their related cousins – the Economic Freedom Fighters (the EFF). Again, a ‘Black’ Pan-African hegemony or identification with it. Dealt a great injustice by ‘Apartheid and Colonisation’ (the Europeans – read ‘whites’) and ‘the struggle’ – i.e. the war, its death and socio-economic destruction and indignation leaves an enduring scar on the psyche on the Black African nation. So that’s the ‘Political’ enemy, now for the economic -‘White Monopoly Capital’ the ‘whites’ profiteering from the capital and minerals rightfully belonging to the Africans and exploiting ‘Black’ labour to do it. The result – a ‘Banana’ Republic run on extreme Nationalist lines to ensure the liberty of the ‘Black’ nation with a very high incidence toward state involvement and control (nationalisation) whilst also drawing compensation from both the state and private concerns for the past economic “hobbling” of a enslaved and exploited black nation (pitched as ‘the previously disenfranchised’).

In Conclusion
Nationalism, whether practiced by African Nationalists or Afrikaner Nationalists are two different peas in the same pod. The current ‘Banana’ Republic is a direct consequence of the Apartheid Republic which came before it. The Apartheid Republic was a consequence of Union, the Union was a consequence of the conflict between Boer Republicanism and British Imperialism.
The ‘Keep South Africa White” Republic pipe-dream of Dr. H.F. Verwoerd and his cabal in 1960 was an abhorrent and short lived testament to Boer independence with disastrous consequences for just about everyone – and Boer Generals like Smuts and Botha recognised the danger of hanging onto this idea from the get-go, General Jan Smuts even going so far as to say of National Party’s concept of Apartheid –
“The idea that the natives must all be removed and confined in their own kraals is in my opinion the greatest nonsense I have ever heard.”
This love affair with Nationalism is ultimately reflected in one of the greatest ironies, but not surprising if we understand Nationalism, when the Afrikaner National Party (NP – repositioned as the ‘New’ NP after 1997) folded up shop on the 5th August 2005 and all their members “walked the floor” to join their African nationalist cousins in the African National Congress (ANC) in coalition and membership. Proof positive of the ideological conjugal bed.
The cyclical nature of history has always shown that minorities cannot hold control over majorities indefinitely – and the two always roll over on one another, and where consensus elects a fiercely Nationalistic government, there is a tendency for that government to gravitate to Kleptocracy – and the Afrikaner Nationalists did it, so too now the African Nationalists – a rule by a elitist grouping (a real minority), consolidating absolute power (which corrupts absolutely) and helping itself to the state’s wealth. History fortunately shows us the majority will eventually see them out again (and the sooner the better for the ‘democratic’ South African Republic really).

This also an historic truism, in the great fight of ‘right’ against ‘wrong’ world over – history has always sided with those who fight for human suffrage and emancipation as been on the side of the morally ‘good’ fight. The defenders of regimes which oppress and deny human suffrage and emancipation are always deemed as been on the side of the morally ‘bad’ fight. The net result has seen regimes like Verwoerd’s Afrikaner Republic come and go, often discarded to the scrapheap of history and irreconcilable within decades, whereas Unions which have individual liberties enshrined in their constitutions tend to last (as bumpy as the road gets at times) – the USA’s Bill of Rights, the Swiss Federal Charter and Bills of Rights and the British Magna Carta and all its subsequent Charters and legal interpretations have generally ensured the survival of these Unions over centuries.
Now, what about ‘Unionism’ were Smuts, Botha, Merriman and their ilk on the right track? Well, consider this, the Southern African Development Community (SADC) comprises all of Smuts’ 3rd Phase ‘Greater South Africa’ countries: Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia and Zimbabwe. And it’s even bigger now as this political, security and economic alliance now also includes the Comoros, Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, Mauritius, Seychelles and Tanzania. Also, strangely enough the ideals of Pan-Africanism as aspired to by the ANC and EFF (and obviously the Pan Africanist Congress) speaks very strongly to a unified African construct.
The mission of SADC is similar to that of the Greater South African Union, that is to promote sustainable and co-dependent and equitable economic growth and socio-economic development throughout the region. The obvious difference, Smuts saw ‘Pretoria’ as the capital and the regional economic driver as Johannesburg, with Federated control from Pretoria (like Washington D.C. controls the USA’s ‘Union’ and New York its business hub) … and, here’s the problem child – only with ‘white civilisation’ guiding progress.
This ‘white stewardship’ of the Victorian period clearly would not work out after World War 2 and with historic hindsight would never have been sustainable going forward, however Jan Smuts played ‘the long game’ – by January 1942, even Jan Smuts had seen the end of ‘white Imperialism’ when he admitted at an Institution of Race Relations conference that “segregation has fallen on evil days” and by the time Smuts drafted and ratified the preamble of another “Union” the United Nations (UN) in October 1945 he was all about human rights and suffrage, subscribing to reaffirming “faith in fundamental human rights, in the dignity and worth of the human person, in the equal rights of men and women and of nations large and small.” (preamble to the UN as drafted by Smuts).
One has to wonder, had Jan Smuts and the Greater South African Union been given time and space, and had the Afrikaner nationalist ideals of a White’s Only Republic not resurfaced as a reality, Apartheid not implemented with such Nationalist vigour, and a less radicalised view of Pan-Africanism in Southern Africa not come around because of Apartheid and Colonial whites clutching onto power once their mandates were well past their ‘sell-by’ dates – whether we would have been on a substantively different trajectory than what we have today … I wonder.
Written and Researched by Peter Dickens