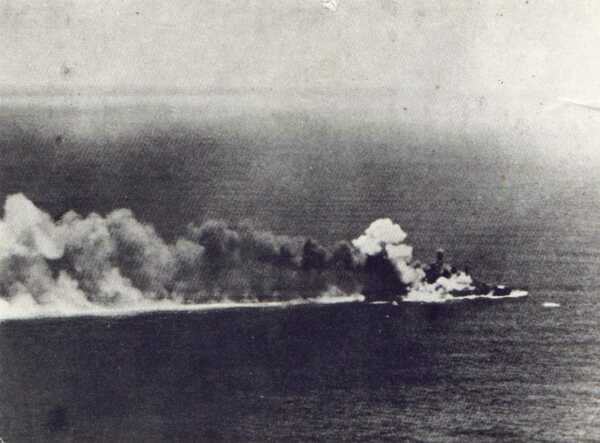
This is an image of the HMS Dorsetshire listing and burning just prior to her sinking, it was attacked by the Imperial Japanese Navy using carrier borne dive bombing aircraft. A large number of South African Navy personnel were involved in the battle and were lost with this ship whilst seconded to the Royal Navy during World War 2.

As Simonstown in South Africa was a British Naval base thousands of South Africans in WW2 served in the Royal Navy as well as in the South African Naval Forces (SANF). The loss of a heavy Cruiser the size of the HMS Dorsetshire is bound to include a South African honour roll and unfortunately this one does – a very long one at that, especially given this particular Battle Cruiser’s long association with South Africa.
The sinking of both the HMS Cornwall and the HMS Dorsetshire in the Indian Ocean by the Japanese on 5th April 1942 is linked. Not only that they were sunk within range of one another on the same day, but also in terms of the relationship of these two ships had with South Africa and the number of South Africans on board. This is further linked to the sinking of the HMS Hermes and HMS Hollyhock later in the same engagement with the Japanese, with similar relations and consequences to the South African Navy.
So, let’s focus on the HMS Dorsetshire today, a hero in the sinking of the German Battleship Bismarck and the extraordinary link between this ship and South Africa.
HMS Dorsetshire Short History
 The HMS Dorsetshire was a heavy cruiser and after commissioning in 1930 became the flagship of the 2nd Cruiser Squadron Atlantic Home Fleet. Before the war, from 1933 until 1936, HMS Dorsetshire served on the Africa Station. Her first recorded docking in the Selborne dry dock at Simonstown, South Africa was on 5 January 1934.
The HMS Dorsetshire was a heavy cruiser and after commissioning in 1930 became the flagship of the 2nd Cruiser Squadron Atlantic Home Fleet. Before the war, from 1933 until 1936, HMS Dorsetshire served on the Africa Station. Her first recorded docking in the Selborne dry dock at Simonstown, South Africa was on 5 January 1934.
When the Second World War broke out HMS Dorestshire had joined the China station and in October 1939 she was joined into the hunt for the German pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee along with the HMS Cornwall. Both were withdrawn from the China station and despatched to Ceylon to form Force I.
In December 1939 the HMS Dorsetshire and HMS Cornwall arrived in South Africa where they embarked many South African volunteers, drawn mainly from Royal Navy Volunteer Reserves (RNVR – South African Division) and South African Naval Reserve Force.
The HMS Dorsetshire was called into pursuit of the German ‘pocket battleship’ Admiral Graf Spee, which having left Wilhemshaven on 21 August 1939 had reached the eastern part of the South Atlantic in early October 1939. In this region she managed to sink three British ships, Newton Beach, Ashlea and Huntsman on 5, 7 and 10 October respectively some 1,000 nautical miles north west of Cape Frio in Namibia, and then the Trevanion 630 miles north west of Walvis Bay on 22 October.
Admiral Graf Spee then continued on south and rounded the Cape passing some 400 miles south of Cape Agulhas. On 15 November she sank the small tanker Africa Shell a mere 10 miles off the coast of Mozambique before moving once again around the Cape keeping at least 300 miles off shore passing Cape Agulhas once more on 3 December 1939.
When the German Battleship ‘Admiral Graf Spee’ was discovered and pursued by the British Royal Navy, the Graf Spee was sent to the River Plate estuary in South America and because of the potential fall-out should it be sunk or captured the Captain was ordered by the German High Command to scuttle his vessel after leaving the Montevideo harbour – without encountering the Royal Navy.
In February 1940 while in the Atlantic, the German supply freighter Wakama was stopped by Dorsetshire in the area off Cabo Frio and her crew scuttled also her . On 2 March 1940 she left the Falklands with wounded from the cruiser HMS Exeter en-route to Cape Town, South Africa. On the 11th , the wounded and the prisoners from the German freighter were all put ashore.
She was then docked again at Simonstown’s Selborne dry dock, prior to sailing back to United Kingdom. This short movie Pathé news reel captures the HMS Dorsetshire in South Africa and its well worth a quick look:
On May 25th, the cruiser arrived in Plymouth in the UK, and at the end of the month sailed for Freetown to commence operations around Dakar in pursuit of the Vichy French Battleship Richelieu. She sailed on again to South Africa and was dry docked in Durban on the 4th September, on the 20th September she arrived back in Simonstown, where a day later she sailed for Sierra Leone.
November saw her in the Indian Ocean where she bombarded Zante in Italian Somaliland. In December Dorsetshire docked once again in the Selborne dry dock in South Africa and later that month she was ordered to search for the German pocket Battleship Admiral Scheer.
On 18 January 1941, HMS Dorsetshire captured the Vichy French freighter Mendoza and escorted the ship to Takaradi. In March 1941, Dorsetshire was once again docked in the Selborne dry dock in South Africa. Late in May 1941, whilst in the North Atlantic on convoy covering duties, HMS Dorsetshire together with the cruiser HMS London were tasked to search for the German Battleship ‘Bismarck’.
The sinking of the Bismarck

The Bismarck
At the time she was ordered to search for the Bismarck on 26th May 1941 the HMS Dorsetshire was some 360 nautical miles (670 km) south of the Bismarck’s actual location. HMS Dorsetshire steamed at top speed, though heavy seas until she encountered the destroyer HMS Cossack, which had been engaging the Bismarck during the night, the German battleship’s gun flashes could be seen six miles away by early morning.
The HMS Dorsetshire then took part in the Bismarck’s final battle, The battleships HMS Rodney and HMS King George V neutralised Bismarck‘s main battery early in the engagement, the HMS Dorsetshire and other warships closed in to join the attack. The HMS Dorsetshire opened fire at a range of 18,00 meters. In the course of the engagement, she fired 254 shells from her main battery. In the final moments of the battle, she was ordered to move closer and torpedo the Bismarck and fired three torpedoes, two of which hit the crippled battleship.
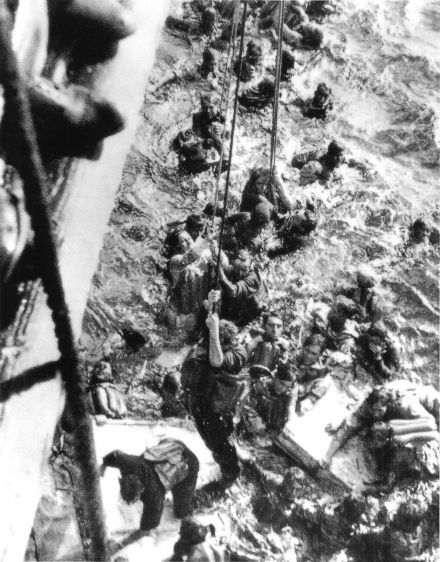

Survivors from Bismarck are pulled aboard Dorsetshire on 27 May 1941
The Germans had by this time also detonated scuttling charges, which also with the damage inflicted by the British Royal Navy, caused the Bismarck to rapidly sink just before midday on the 27th May 1941.
The HMS Dorsetshire and the destroyer HMS Maori were tasked to pick up survivors. A reported U-boat sighting forced the two ships to break off the rescue effort, after picking up only 110 men: 85 aboard Dorsetshire and 25 aboard Maori.
African Duties and Raiders
In late August, HMS Dorsetshire left Freetown and participated in the unsuccessful search for the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper, On the 4th November HMS Dorsetshire sent to investigate reports of a German surface raider in the South Atlantic with no result.
After arriving again in Cape Town on 9 December 1941, having sunk a German U Boat supply ship the ‘Python’ whilst she was refuelling a pair of German U-boats.
Beginning 1942, HMS Dorsetshire, under the command of Augustus Agar was assigned to the Eastern Fleet in the Indian Ocean.
The Easter Sunday Raid
With Japan’s entry into the war, and especially after the fall of Singapore, Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) became a front-line British base. The Royal Navy’s East Indies Station and Eastern Fleet was moved to Colombo and Trincomalee.
Admiral Sir James Somerville was appointed as the commander of the British Eastern Fleet, and he decided to withdraw main component the fleet to Addu Atoll in the Maldives, leaving a small force to defend Ceylon (Sri Lanka) consisting of an aircraft carrier, the HMS Hermes, two heavy cruisers – the HMS Cornwall and HMS Dorsetshire, one Australian Destroyer the HMSAS Vampire and the flower class corvette, the HMS Hollyhock.
The Royal Navy’s own ‘Pearl Harbour’
The Imperial Japanese Navy, in much the same way and with the same objectives that were used at Pearl Harbour against the American fleet planned a decisive attack of the British Eastern Fleet to end their presence in the North Indian and Pacific oceans. Unaware that the main body of the British fleet had moved to the Maldives, they focused their plan on Colombo (the commercial capital of modern-day Sri Lanka).
The planned Japanese attack was to become collectively known as the Easter Sunday Raid and the Japanese fleet comprised five aircraft carriers plus supporting ships under the command of Admiral Chuichi Nagumo.
In an almost exact copy of the raid on the American fleet at Peal Harbour (as if no learnings were made by the Allies), on 4 April 1942, the Japanese fleet was located by a Canadian PBY Calatina aircraft, the Catalina radioed the position of the Japanese Fleet to The British Eastern Fleet which alerted the British to the impending attack before it was shot down by six Japanese Zero fighters from the carrier Hiryu.

A Mitsubishi A6M Zero fighter plane takes off from the deck of the Japanese aircraft carrier Akagi, part of the Japanese Naval force in the Indian Ocean
However, despite the warning Nagumo’s air strike on Colombo the next day, Easter Sunday 5th April 1942 they did manage to achieved near-complete surprise (Pearl Harbour was also attacked on a weekend). The British Radar installations were not operating, they were shut down for routine maintenance (another parallel with the attack on Peal Harbour).

Captain Mitsuo Fuchida
The first attack wave of Japanese planes took off in pre-dawn darkness (30 minutes before sunrise) from the aircraft carriers Akagi, Hiryu and Soryu, moving about 200 miles south of Sri Lanka. The first attack wave of 36 fighters, 54 dive bombers, and 90 level bombers was led by Captain Mitsuo Fuchida the same officer who led the air attack on Pearl Harbour.
The Heavy Cruisers, HMS Cornwall and HMS Dorsetshire set out in pursuit of the Japanese. On 5 April 1942, the two cruisers were sighted by a spotter plane from the Japanese cruiser Tone about 200 miles (370 km) southwest of Ceylon. A wave of Japanese dive bombers led by Lieutenant Commander Egusa took off from Japanese carriers to attack Cornwall and Dorsetshire, 320 km (170 nmi; 200 mi) southwest of Ceylon, to sink the two ships.
In the attack, the Japanese airman flying Japanese D3A-1 ‘VAL’ dive bombers, a total of 53 dive bombers in the attack wave, dropped 10 bombs on the HMS Dorsetshire itself (250- and 550-pound bombs) and 8 near misses, all in the span of 8 minutes. One of the bombs detonated an ammunition magazine and contributed to her rapid sinking. Of the two British cruisers, the HMS Dorsetshire sank first, with her stern going first at about 13:50, the HMS Cornwall was hit eight times and sank bow first about ten minutes later.
An eye-witness account from a South African Seaman on board the HMS Dorsetshire recounts the ferocity and nature of the Japanese attack:
Seaman WJ Spickett of Cape Town South Africa who was on lookout duty on Dorsetshire saw the whole action from start to finish.
“We were steaming to keep a rendezvous and when about 400 miles off land, a seaplane which we could not identify, started shadowing us. This was about 10 o’clock in the morning. Dorsetshire and Cornwall were steaming fast, keeping about four miles apart. At 20 minutes to two we spotted a large formation of between 40 and 60 aircraft coming towards us. Within a few minutes they were overhead — so high they were mere specks. Then they came straight for us in formations of three, diving at such a steep angle that it was impossible for our guns to get at them.
I saw the first bomb, a silvery flash in the sunlight, come straight for us. It was a direct hit, blasting our aircraft platform to pieces. In that first attack, I think 10 bombs were dropped. We were steaming at high-speed but eight of those 10 were direct hits. The other two were near misses. The ship listed badly and within 10 minutes of the first bomb being dropped we got orders to abandon ship.
We got away two whalers and a skiff and several rafts. There were hundreds of us in the water and then three planes came over and added to the horror of these moments ‘. Many were killed and wounded in this attack but apparently it was just a gesture of victory for it was not repeated.”
This witness account of machine gunning the survivors in the water is verified by a number of survivors including the Engineering Officer Lieutenant E. A. Drew, who said that whilst in the water they were “subjected to machine gun fire from the large number of Japanese planes that hung around until the ship sank”.

Japanese combat photograph showing the Royal Navy heavy cruisers HMS Dorsetshire and HMS Cornwall on fire and sinking
Survival and Sacrifice
In all the survivors of the sinking of both the Cornwall and Dorsetshire spent over 30 hours in the water clinging to debris or huddled in life rafts. Many seriously injured and burned and during the night ‘space’ was made available on the tiny rafts and flotsam for many clinging onto them as many of their colleagues succumbed to their wounds. Being the Indian ocean there are also tales of sharks circling the men and even taking them. Harrowing would be an understatement.
Between the two ships, 1,122 men out of a total of 1,546 were picked up by the cruiser HMS Enterprise and the destroyers HMS Paladin and HMS Panther the next day. In this action, of the 424 members of the ships’ companies of the two cruisers who lost their lives, over 42 were South Africans.

Survivors from the HMS Dorsetshire and HMS Cornwall in the water
Because of his ship’s long association with South Africa, a very high proportion of the losses were from the South African Naval Forces. Here is the South African Naval Forces honour roll (MPK means ‘Missing Presumed Killed’) from the sinking;
HMS Dorsetshire – South African Navy Personnel Lost, Honour Roll
 BELL, Douglas S, Ty/Act/Leading Stoker, 67243 (SANF), MPK
BELL, Douglas S, Ty/Act/Leading Stoker, 67243 (SANF), MPK
BRUCE, Alexander M, Stoker 2c, 67907 (SANF), MPK
EVENPOEL, Albert, Stoker 2c, 67909 (SANF), MPK
GEFFEN, Sender, Stoker 1c, 68035 (SANF), MPK
HOWE, Horace G, Ordinary Seaman RNVR, 68680 (SANF), MPK
KENDRICK, George, Stoker 2c, 67910 (SANF), MPK
MCINTYRE, Norman G, Able Seaman, 67446 (SANF), MPK
MCLELLAN, Robert, Ordinary Telegraphist, 67897 (SANF), MPK
MORROW, Douglas E, Able Seaman, 67989 (SANF), MPK
ORTON, Charles P, Able Seaman, 68009 (SANF), MPK
REDMAN, Roland A, Leading Stoker, 67406 (SANF), MPK
SCOTT, William J, Able Seaman, 68007 (SANF), MPK
SEVEL, Harry, Stoker 1c, 68100 (SANF), MPK
WILLETT, Amos A S, Stoker 1c, 67240 (SANF), MPK
WILLIAMSON, Walter N, Able Seaman, 67803 (SANF), MPK
HMS Dorsetshire – South African’s lost serving in the Royal Navy, Honour Roll
CONCANON, Harold Bernard, Surgeon Lieutenant (Doctor)
MILNE, Lawrence Victor, Able Seaman
VAN ZYL, David Isak Stephanus, Stoker 1st Class
WILLETT, Amos Alfred Sidney ,Stoker 1st Class
Note: Some more South Africans may not accounted in the above list as they may have been Royal Navy personnel having volunteered to serve in the Royal Navy, there is a long list of South Africans not accounted on the Navy’s honour rolls because of the complication of citizenship, the position of the South African Union in supporting the war and the nature of Simonstown near Cape Town as ‘British territory’ and not South African.
Related work
The Japanese Easter raid was to bring a terrible toll on not only the Royal Navy, but also on the South African Navy whose personnel were involved. It remains the South African Navy’s darkest days, as not only were the HMS Cornwall and HMS Dorsetshire full of SANF personnel. For a full article on the HMS Cornwall, click on this link (“A terrific explosion lifted the ship out of the water”; Recounting South African sacrifice on the HMS Cornwall).
So too were the other two ships sunk later in this engagement on the 9th April 1942 by the same Japanese raiders, with similar South African naval personnel losses – the HMS Hermes, see related article by clicking this link (“Dante’s Inferno”; Recounting South African sacrifice on the HMS Hermes) and HMS Hollyhock, see related article by clicking this link ( “She immediately blew up”; Recounting South African sacrifice on the HMS Hollyhock).
In Conclusion
This history is lost to most South Africans, however good work is now been done by a handful of individuals to try and correct and up-date these honour rolls and recount the full depth of South Africa’s involvement in warfare at sea during World War 2.
That the history is lost is due to the political expediency of the National Party, who on acent to power after WW2, effectively wiped it clean of the national consciousness – branding our World War 2 veterans as ‘traitors’ instead of ‘heroes’ for serving a British cause in their estimation. It is further lost to the new generations due to the slow up-take in recognition if this history by the African National Congress (ANC) government, again for their own political expediency.
That the darkest days of the South African Navy – The Easter Raid of 1942, is not even officially acknowledged or even remembered by The South African Navy in our modern day is testament to this and the subject of a future Observation Post article.
We, as South Africans, do however have an excellent tradition at the Selborne Graving Dock, the dry docks in Simonstown, allowing visiting crews to paint their ships emblems on the docks walls, it is an excellent record of many of the proud Royal Navy fighting ships who visited our shores in World War 2 and on whom many South Africans served. Next time you are there look out them, including the HMS Dorsetshire.
 Their names have not been forgotten.
Their names have not been forgotten.
Researched by Peter Dickens. Background on HMS Dorsetshire extracted from U Boat.net. Wikipedia. News reel copyright British Pathé. British Broadcast Corporation account on the war (BBC) WW2 The Peoples War. Casualty Lists of the Royal Navy and Dominion Navies, World War 2 by Don Kindell. Extracts fro ‘Day to Day SA Naval History’ by Chris Bennett. Thanks also to Graham Du Toit for his excellent research into the Honour Roll including South Africans serving in the Royal Navy.


Pingback: “A terrific explosion lifted the ship out of the water”; Recounting South African sacrifice on the HMS Cornwall | The Observation Post
Pingback: The South African Navy’s ‘darkest hour’ is not recognised and not commemorated | The Observation Post
Pingback: The South African Navy’s ‘elephant in the room’ | The Observation Post
Pingback: Global Maritime History Royal Navy Cruisers (2): HMS Dorsetshire, All around the Empire in twelve years! - Global Maritime History
Fascinating reading as my late Dad,Gabriel Sheen,a writer ,was assigned to the captain, was one of the South African survivors of HMS Dorsetshire.
LikeLike
I would like to know if you have information regarding my father Percival Maurice Fry who I think was on board the HMS DORSETSHIRE when it was attacked and sank. He did survive and was rescued but I never asked him the name of the ship he was on. He has since passed on. Monica Jackson née Fry.
LikeLike
My apologies for not mentioning in my request I submitted earlier. I should have mentioned that my dad was a South African from Durban Natal, now Kwa Zulu Natal. He was in the Navy, possibly the South African Navy or he could have been seconded to the British Navy. Regards Monica Jackson.
LikeLike